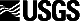


| Vent | Tephra | Pyroclastic flows | Lava flows | |||||
| length km |
area km2 |
volume km3 |
length km |
area km2 |
volume km3 |
area km2 |
volume km3 |
|
| Glass Creek | > 190 | > 9,000 | 0.10 | -- | --- | ---- | 1.0 | 0.10 |
| Obsidian | > 25 | > 140 | 0.02 | < 2 | --- | ---- | 1.8 | 0.17 |
| South Deadman1 |
> 20 | > 220 | 0.05 | 6 | > 15 | 0.05 | 1.1 | 0.13 |
1 Two tephra lobes were produced during the explosive activity of South Deadman vent; the values reported represent combined area covered and volume erupted.
|
The eruption of magma in the form of tephra (chiefly pumice and volcanic ash), pyroclastic flows, and lava flows occurred about 600 years ago from the Inyo chain at the Glass Creek, Obsidian, and South Deadman vents. The entire eruption sequence generated about 0.22 km3 of explosive rock debris and extruded about 0.4 km3 onto the ground. The volumes reported here from C.D. Miller (see reference below) are dense rock equivalent (volume of magma below ground). |
Miller, C.D., 1985, Holocene eruptions at the Inyo volcanic chain, California -- implications for possible eruptions in the Long Valley caldera: Geology, v. 13, pp. 14-17.

