Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB)
Diminishing Options for Treatment
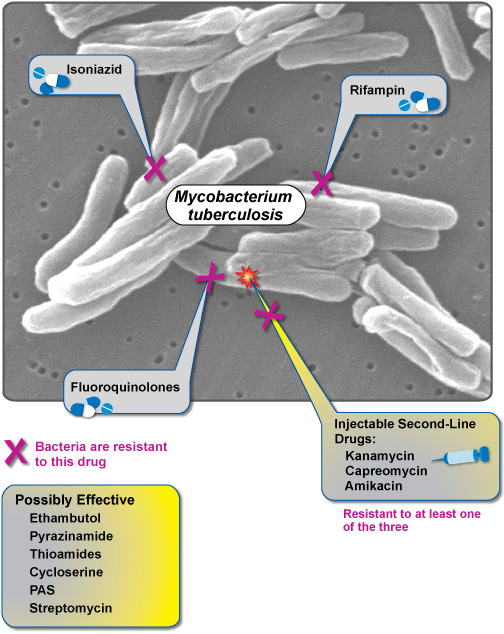
XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above. XDR TB strains may also be resistant to additional drugs, greatly complicating therapy. Click here to see how these drugs work.


Drug-Resistant TB—A Visual Tour
 First-Line Treatment of Tuberculosis (TB) for Drug-Sensitive TB
First-Line Treatment of Tuberculosis (TB) for Drug-Sensitive TB
 Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR TB) and Possible Effective Treatments
Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR TB) and Possible Effective Treatments
 Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB) Diminishing Options for Treatment
Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis (XDR TB) Diminishing Options for Treatment
 New Tuberculosis Drugs Under Development
New Tuberculosis Drugs Under Development
Learn More
 TB Definitions
TB Definitions
 Scientific Illustrations of Drug-Resistant TB
Scientific Illustrations of Drug-Resistant TB
 TB Home Page
TB Home Page
Photo Credit: The photo of Mycobacterium tuberculosis was obtained from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC/ Dr. Ray Butler; Janice Carr.
Illustration Credit: This illustration is in the public domain. Please credit the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
Illustrator: Krista Townsend