|
 |
 |
||
    |
||||
|
||||
|
Other Health Topics: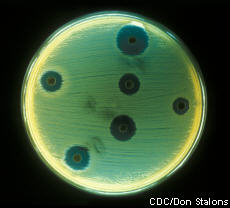
MRSA
Also called: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It causes an infection that is resistant to several common antibiotics. There are two types of infection. Hospital-associated MRSA happens to people in healthcare settings. Community-associated MRSA happens to people who have close skin-to-skin contact with others, such as athletes involved in football and wrestling. Infection control is key to stopping MRSA in hospitals. To prevent community-associated MRSA
If a wound appears to be infected, see a healthcare provider. Treatment may include draining the infection and antibiotics. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Start Here
|
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Disclaimers | Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 27 April 2009 Topic last reviewed: 19 November 2008 |