|
 |
 |
||
    |
||||
|
||||
|
Other Health Topics: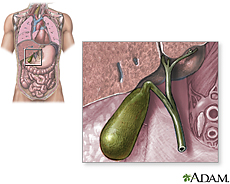
Gallstones
Also called: Cholelithiasis
Your gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ under your liver. It stores bile, a fluid made by your liver to digest fat. As your stomach and intestines digest food, your gallbladder releases bile through a tube called the common bile duct. The duct connects your gallbladder and liver to your small intestine. Your gallbladder is most likely to give you trouble if something blocks the flow of bile through the bile ducts. That is usually a gallstone. Gallstones form when substances in bile harden. Gallstone attacks usually happen after you eat. Signs of a gallstone attack may include nausea, vomiting, or pain in the abdomen, back, or just under the right arm. Gallstones are most common among older adults, women, overweight people, Native Americans and Mexican Americans. The most common treatment is removal of the gallbladder. Fortunately, the gallbladder is an organ that you can live without. Bile has other ways to reach your small intestine. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Start Here
|
| Home | Health Topics | Drugs & Supplements | Encyclopedia | Dictionary | News | Directories | Other Resources | |
| Disclaimers | Copyright | Privacy | Accessibility | Quality Guidelines U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD 20894 National Institutes of Health | Department of Health & Human Services |
Date last updated: 08 May 2009 Topic last reviewed: 27 December 2008 |