Image Library
These high-resolution (300 dpi) images may be downloaded directly from this site. All images, except those specified as World Health Organization (WHO) images, are in the public domain. For the public domain images, there is no copyright, no permission required, and no charge for their use.
We thank the organizations that provided these images and, if you use them, we ask that you credit the source. To obtain permission for WHO images, complete and submit the form at the bottom of the WHO copyright page.
For images not found here, visit the Center for Disease Control and Prevention's public health image library.
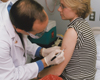 |
Smallpox Vaccination Study-1
Smallpox vaccination dilution study: Dr. John Treanor draws circle on volunteer's arm so he can later locate the exact spot where he applied the vaccine.
Credit: University of Rochester School of Medicine |
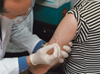 |
Smallpox Vaccination Study-2
Smallpox vaccination dilution study: Dr. John Treanor uses a two-pronged needle to deliver the smallpox vaccine into the arm of a volunteer.
Credit: University of Rochester School of Medicine |
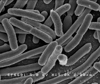 |
Escherichia coli
Scanning electron micrograph of Escherichia coli, grown in culture and adhered to a cover slip.
Credit: Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH |
 |
Yersinia pestis
Scanning electron micrograph depicting a mass of Yersinia pestis bacteria (the cause of bubonic plague) in the foregut of the flea vector.
Credit: Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH |
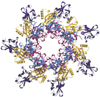 |
Anthrax Structure
Anthrax heptamer structure.
Credit: R. John Collier, Harvard Medical School |
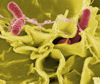 |
Salmonella
Color-enhanced scanning electron micrograph showing Salmonella typhimurium (red) invading cultured human cells.
Credit: Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH |
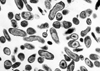 |
Q Fever
Coxiella burnetii, the bacteria that causes Q fever.
Credit: Rocky Mountain Laboratories, NIAID, NIH |
 |
BSL-4 Lab, Protective Gear
BSL-4 laboratory worker wearing protective gear.
Credit: USAMRIID, DoD |
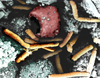 |
Anthrax
Color-enhanced scanning electron micrograph shows splenic tissue from a monkey with inhalational anthrax; featured are rod-shaped bacilli (yellow) and an erythrocyte (red).
Credit: Arthur Friedlander |
Images from WHO
All images below are copyright protected by WHO. To obtain permission for these images, complete and submit the form at the bottom of the WHO copyright page. |
 |
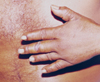
Smallpox Vaccination
Use of bifurcated needle for multipuncture smallpox vaccination.
Credit: WHO |
 |
Cutaneous Anthrax
Cutaneous anthrax lesions on a man infected with the bacterium Bacillus anthracis.
Copyright: WHO |
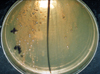 |
Anthrax in Culture Dish
Colony of Bacillus anthracis on selective agar plate after 42 hours at 37°C.
Copyright: WHO |
 |
Anthrax in the Wild
Gazelle killed by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis, which causes anthrax.
Copyright: WHO |
back to top