|
|
 |
Immune Cells
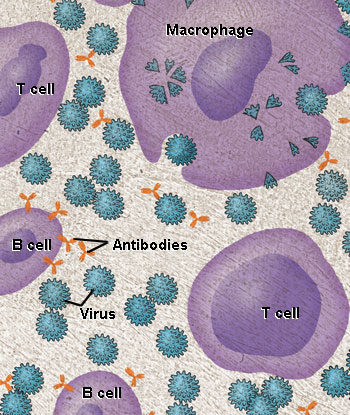 |
| Most vaccines help prevent disease by mimicking the immune system's natural response to infection. In the body, cells called macrophages engulf invading microbes, such as viruses, and sound the alarm by showing pieces of the invader to T cells and B cells. B cells produce defensive molecules called antibodies that “stick” to the microbes, making them unable to multiply and cause disease. For more information, read How Vaccines Work. | |
|