The Network
CPTAC Team Network
Collaborations with Federal and International Agencies
All Organizations Participating in the CPTC Initiative
CPTAC Team Network
The Clinical Proteomic Technology Assessment for Cancer (CPTAC) team network extends well beyond the five centers, bringing in expertise from both the public and private sectors to ensure that all of the expertise needed is brought together in a single focus.
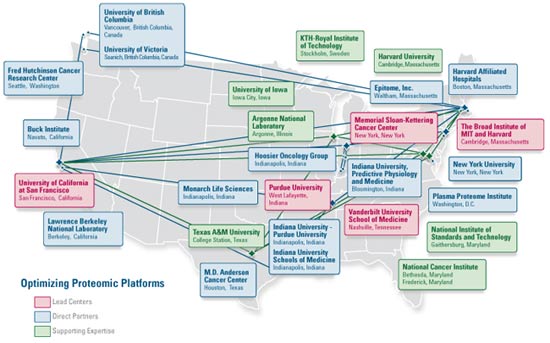
Click here to view large map
Collaborations with Federal and International Agencies
The CPTC is designed to enable infrastructure development to support clinical proteomics experiments. As such, the goals of the Initiative seek to provide a broadly applicable set of tools amenable to wide use by the research community. To facilitate this mission, the NCI has formed several strategic collaborations with Federal and international agencies, including:
![]() Argonne National Laboratories (ANL)
Argonne National Laboratories (ANL)
![]() Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB) at the University of Iowa
Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB) at the University of Iowa
![]() European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI)
European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI)
![]() Harvard Institute of Proteomics (HIP)
Harvard Institute of Proteomics (HIP)
![]() National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
 Argonne National Laboratories (ANL)
Argonne National Laboratories (ANL)
NCI has formed an Interagency Agreement with ANL to produce ~100 well-characterized cancer-related proteins for use in antibody production, affinity capture technology development, and creation of reagent protein standards. In addition, a "Protein ID-to-Antibody Production" Workflow is being explored that begins with protein target acquisition and uses publicly available clones/expression vectors to produce proteins, which can then be characterized and their data submitted to a public database. Such a strategy will establish a new quality assessment/quality control (QA/QC) standard for protein/antibody development for the clinical proteomics community. These proteins will be used for a variety of purposes, including antigen development, proteomics platform assessment, and standards development.
To learn more about ANL visit http://www.anl.gov.
 Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB) at the
Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB) at the
University of Iowa
The University of Iowa’s Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank (DSHB) collects, stores, grows, and distributes all hybridomas and monoclonal antibodies from the Clinical Proteomic Technologies for Cancer programs. The DSHB was established to supply investigators with monoclonal antibodies useful for studies in developmental and cell biology, which may be ordered as tissue culture supernatants, ascites, or concentrate; selected hybridomas are also available as frozen or growing cells.
To learn more about the University of Iowa Hybridoma Bank, visit: http://dshb.biology.uiowa.edu.
 European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI)
European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI)
The Clinical Proteomic Technologies for Cancer initiative is also working closely with the EBI to coordinate bioinformatics standards development for clinical proteomics. The EBI is a non-profit academic organization associated with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory that manages databases of biological data, including nucleic acids, protein sequences, and macromolecular structures. It is the premier center for research and services in bioinformatics in the European Union (EU). Recently, the EBI invited the Clinical Proteomic Technologies for Cancer initiative to serve as an Associate Partner to Proteomics Data Collection (ProDaC), a recently awarded grant from the EU to the EBI. The ProDaC program will develop international data standards with recommendations from the HUPO-PSI. The NCI is the only Federal research agency invited to participate in this program as an associate partner.
To learn more about EBI visit http://www.ebi.ac.uk.
 Harvard Institute of Proteomics (HIP)
Harvard Institute of Proteomics (HIP)
The Harvard Institute of Proteomics (HIP) applies Nucleic Acid Programmable Protein Arrays (NAPPA) technology to hydriomas and monoclonal antibodies from the Clinical Proteomic Technologies for Cancer programs. HIP has taken the next step after the Human Genome Project by cloning all available human genes in a standard form that enables full-length, high throughput protein expression. By developing and applying new resources and technologies, HIP enables the study of proteins on a genome-wide scale using informatics and automation. The Institute has produced over fifteen thousand clones to date.
To learn more about the Harvard Institute of Proteomics, visit: http://www.hip.harvard.edu.
 Human Protein Atlas (HPA)
Human Protein Atlas (HPA)
After hybridomas and monoclonal antibodies produced from the Clinical Proteomic Technologies for Cancer programs are first characterized by the antibody characterization center at NCI-Frederick, they are further characterized using tissue microarrays at the Human Protein Atlas (HPA). The HPA is a well-recognized, mature resource for tissue microarray analysis expression data for thousands of antibodies across hundreds of normal human tissues and cancer cells. The data is publicly available and presented as high resolution images of immunohistochemically stained tissues and cell lines annotated with links to proteins for specific genes or by browsing individual chromosomes.
To learn more about the Human Protein Atlas, visit: http://www.proteinatlas.org.
 National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
NCI has entered into an Interagency Agreement with NIST to develop MS assessment materials to be used by the CPTAC teams. These materials, designed to assess the performance metrics of various instruments, will be the first of their kind developed by the NCI and will help to evaluate and compare existing proteomic technologies and compare these with emerging proteomic technologies of interest to the clinical cancer community.
To learn more about NIST visit http://www.NIST.gov.
All Organizations Participating in the CPTC Initiative
Accacia International, Inc.
Allele Biotechnology & Pharmaceuticals
Argonne National Laboratory
Battelle Pacific Northwest Laboratories
The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Proteomic Platform and Cancer Program
Buck Institute for Age Research
California Pacific Medical Center
College of William and Mary
Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank at the University of Iowa
Discovery Park at Purdue University
Emory University
Epitome, Inc.
European Bioinformatics Institute
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and its clinical and research partners, the University of Washington and Children’s Hospital and Regional Medical Center
Harvard Institute of Proteomics
Harvard University and its affiliated hospitals (including Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Massachusetts General Hospital)
Hoosier Oncology Group
Human Protein Atlas (KTH – Royal Institute of Technology; Stockholm, Sweden)
Indiana University
Indiana University School of Medicine
Indiana University – Purdue University Indianapolis
Institute for Systems Biology
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
Meso Scale Diagnostics
Michigan State University
Monarch Life Sciences
National Cancer Institute – Center for Cancer Research Tissue Array Program
National Cancer Institute – Frederick Advanced Technology Program
National Institute of Standards and Technology
New York University Medical Center
Northeastern University
Plasma Proteome Institute
Predictive Physiology and Medicine, Inc.
Purdue University
Quadraspec, Inc.
Rules-Based Medicine, Inc.
Sequenom, Inc.
University of British Columbia
University of California, Los Angeles
University of California, San Francisco
University of Colorado at Boulder
University of Houston
University of Maryland, College Park
University of Michigan
University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center
University of Victoria (UVic-Genome BC Proteomics Center at Vancouver Island Technology Park and Development of Biochemistry and Microbiology)
University of Virginia
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center

