Home > Research > Quantum Grants Quantum Grant SummaryImproving Dialysis Patients' Quality of Life with Miniature Artificial Kidney Principal Investigator
Nearly half a million people in the United States suffer from end-state renal disease (ESRD), and the incidence rate of this disease has been steadily increasing for over 25 years. Kidney transplantation provides the best option for ESRD patients, but a shortage of donors means that most patients never make it to the top of a waiting list. The alternative is dialysis, which is not only expensive and inconvenient for patients, but also far less effective. An interdisciplinary group of researchers from a number of academic institutions and companies has envisioned a way to improve management of ESRD by developing an implantable, self-regulating, bioartificial device capable of filtering toxins from the blood, as well as replacing the endocrine and metabolic functions of the kidney. Current efforts in the design of this two-chamber renal device focus on carefully tailoring the pores of the filtration membrane that can be driven by a patient's normal blood flow. The next step will be the development of a miniaturized cell bioreactor to carry out the other functions of the device. The team hopes to have a product ready for testing in humans within the next 10 years. Back to Quantum Grants Program Main Page |
 |
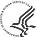 |
Department of Health and Human Services |
 |
National Institutes of Health |
 |