Modules Details Details of Grant Process Modules
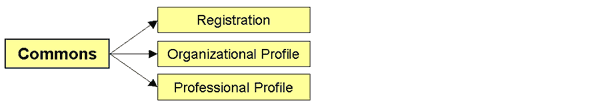
NIH eRA Commons: To begin interacting with NIH, individuals and research organizations register with the NIH eRA Commons. Administrative officials fill in an organizational profile and financial, assurance, and certification information; principal investigators complete a professional profile, contact information, and biosketch.


Competitive Grant Application (CGAP): In the future, the applicant's organization will send an electronic grant application (PHS 398) to NIH in HTML, EDI, XML, or PDF format.


Receipt, Referral, Assignment (RR): NIH's Center for Scientific Review staff use this module to log an application, refer it to an institute, and assign it to an initial review group.


Committee Management (CM): This module allows committee management staff to enter data, query, and prepare reports for managing chartered advisory committees and review meetings. CM is used in conjunction with Review (REV).


Review (REV): For the next step, NIH review organizations use the REV module to access application data and generate lists of prospective reviewers and committee rosters, assign reviewers to applications, score applications, review meeting outcomes, and prepare summary statements.

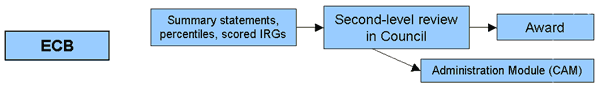
Electronic Council Book (ECB): To perform second-level review, advisory council members and NIH staff use separate versions of this Web-based application. ECB houses summary statements, percentiles, priority scores, initial review groups, and key identifying information for applications going to institute advisory councils for second-level review.


Grants Management (GM): After an award is made, GM lets Grants Management offices process grant awards, assign grants to grants management staff, and view workload.

Status (Commons Status): This is a secure, interactive Web interface by which grantees and grantee organization administrative officials may obtain information about pending grant applications and awards.

eSNAP (Electronic Streamlined Non-Competing Award Process): In the ensuing years of a grant, eSNAP allows PIs to electronically prepare, and administrative officials from grantee organizations to electronically approve and submit, information consistent with the Application for Continuation of a Public Health Service Grant (PHS 2590). In the future, CNAP (Complex Non-Competing Award Process) will be available.

iEdison: Grantee institution technical transfer offices use this interagency website to report inventions developed with government funding.
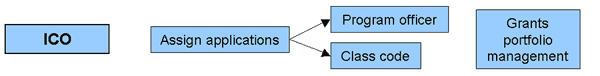
Institute and Center Operations (ICO): This module allows program officers to manage their portfolios, referral officers to assign program class code and grant applications to a program officer, budget officers to indicate grants to be paid, and council administrators to add council actions to the database. ICO also allows internal electronic approval of awards.
Grant Update Module (GUM): This component of the GM, ICO, and REV IMPAC II modules lets authorized users change grant-related data in several dozen fields. Special Initiatives Tracking System (SITS): An IMPAC II module, SITS enables reviewers, grants management, and other NIH staff to access information and functions for special initiatives for minority supplements, disability supplements, and reentry supplements. People: NIH staff use this module to find biosketches and contact information for grantees. User Administration (UA): NIH IMPAC II coordinators use UA to administer user accounts and passwords. Details of Training ModulesX-Train: Using this module, directors and trainees from institutions with National Research Service Awards can transmit personal data electronically to NIH. Training Activities (TA): This module allows NIH staff to process and track appointments, terminations, and payback obligations for National Research Service Awards. Details of Tools for Reports and QueriesCRISP (Computer Retrieval of Information on Scientific Projects) -- CRISP on the Web: This public database of federally funded biomedical research projects allows keyword searching of scientific concepts, projects, and investigators from a database of awards funded since 1972. Users can perform full-text searching of abstracts and grantee organization information. CRISP Plus, the internal IMPAC II version, lets NIH staff obtain sensitive information (e.g., dollar amounts and information on unfunded grants) not available in the external version of CRISP. QuickView (QV): Used by NIH staff, this query tool simplifies retrieval of select grant data, including summary statements, abstracts, basic administrative data, budget information, PI contact information, and notice of grant awards. PowerView (PV): Power Views are pre-joined tables accessible for reporting, analysis, and evaluation, using various query tools, including Microsoft Access and Excel. PV provides a more powerful way to download grant-related information from IMPAC II. IC Query and Reporting (IQR): This IMPAC II module is a high-end reporting tool for accessing the IRDB (IMPAC II Reporting Database).
|