caGrid and Infrastructure Overview
|
What is caGrid?
caGrid (or the Grid) is an Architecture development project that provides the core infrastructure and tooling needed to connect to the Grid - this is the ultimate target of the compatibility process. caGrid is the underlying network architecture that provides the basis for connectivity between all of the cancer community institutions, allowing research groups to tap into the rich collection of emerging cancer research data while supporting their individual investigations. caGrid manages and securely shares information and analytic resources using locally managed access control policies and by using strongly typed data objects in XML format.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Sharing of resources (computational, storage, data, etc.)
- Secure Access (global authentication, local authorization, policies, trust, etc.)
- Open Standards Virtualization
Getting on the Grid: Advertising and Discovering Services
“Getting something on the Grid” – or “establishing a Grid node” – means meeting requirements for interoperability (through adoption or adaptation), and then connecting that interoperable service or data source to a Grid (internal or external). Grid services are “advertised” through an index. You can also connect to a Grid to “discover” services or data provided by others.
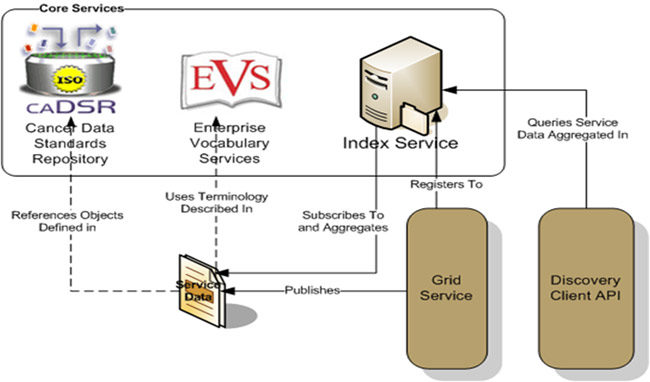
Infrastructure - the informatics backbone of caGrid
Core services – including data standards, shared vocabularies, and indexing – provide the critical elements needed to advertise and discover other Grid resources.
|
To Grid-enable a system (expose a compatible tool on the Grid) you must:
- Use object types and information models registered in the caDSR. Develop object oriented APIs and data resources.
- Define a Grid service interface that defines the functionality that you are exposing to the Grid. This grid service interface uses the same object types as your existing system, but represents them in a way that is platform and language neutral (e.g., using XML).
- Complete Grid service implementation by mapping service invocations to API calls or queries into the existing system.
- All of these activities are enabled through caGrid tools and infrastructure – adopting a caBIG™ compatible tool means much of the work has already been done for you – adaptation may take more effort.
You cannot “get your tool on the Grid” unless you have: (1) adopted or adapted a tool that is caBIG™ compatible; (2) Installed caGrid software.
