
|

What does MDMA do
to the brain?
MDMA affects the brain by increasing the activity of at least three neurotransmitters (the chemical messengers of brain cells): serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.5 Like other amphetamines, MDMA causes these neurotransmitters to be released from their storage sites in neurons, resulting in increased neurotransmitter activity. Compared to the very potent stimulant, methamphetamine, MDMA causes greater serotonin release and somewhat lesser dopamine release.18 Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in the regulation of mood, sleep, pain, appetite, and other behaviors. The excess release of serotonin by MDMA likely causes the mood elevating effects experienced by MDMA users. However, by releasing large amounts of serotonin, MDMA causes the brain to become significantly depleted of this important neurotransmitter, contributing to the negative behavioral aftereffects that users often experience for several days after taking MDMA.19
Numerous studies in animals have demonstrated that MDMA can damage serotonin-containing neurons;1,3 some of these studies have shown these effects to be long lasting. This suggests that such damage may occur in humans as well; however, measuring serotonin damage in humans is more difficult. Studies have shown that some heavy MDMA users experience longlasting confusion, depression, and selective impairment of working memory and attention processes.20,21,22,23,24 Such memory impairments have been associated with a decrease in serotonin metabolites or other markers of serotonin function. Imaging studies in MDMA users20,22,25 have shown changes in brain activity in regions involved in cognition, emotion, and motor function.26,27,28 However, improved imaging technologies and more research are needed to confirm these findings and to elucidate the exact nature of the effects of MDMA on the human brain.
It is also important to keep in mind that many users of ecstasy may unknowingly be taking other drugs that are sold as ecstasy, and/or they may intentionally use other drugs, such as marijuana, which could contribute to these behavioral effects. Additionally, most studies in people do not have behavioral measures from before the users began taking drugs, making it difficult to rule out pre-existing conditions.21,29,30 Factors such as gender, dosage, frequency and intensity of use, age at which use began, the use of other drugs, as well as genetic and environmental factors all may play a role in some of the cognitive deficits that result from MDMA use and should be taken into consideration when studying the effects of MDMA in humans.
Given that most MDMA users are young and in their reproductive years, it is possible that some female users may be pregnant when they take MDMA, either inadvertently or intentionally because of the misperception that it is a safe drug. The potential adverse effects of MDMA on the developing fetus are of great concern. Behavioral studies in animals have found significant adverse effects on tests of learning and memory from exposure to MDMA during a developmental period equivalent to the third trimester in humans.31 However, the effects of MDMA on animals earlier in development are unclear;32,33 therefore, more research is needed to determine what the effects of MDMA are on the developing human nervous system.
|
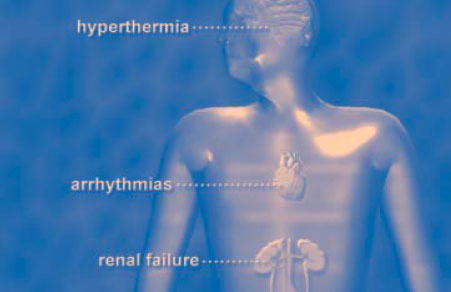 |
Is MDMA Addictive?
For some people, MDMA can be addictive. A survey of young adult and adolescent MDMA users found that 43 percent of those who reported ecstasy use met the accepted diagnostic criteria for dependence, as evidenced by continued use despite knowledge of physical or psychological harm, withdrawal effects, and tolerance (or diminished response), and 34 percent met the criteria for drug abuse. Almost 60 percent of people who use MDMA report withdrawal symptoms, including fatigue, loss of appetite, depressed feelings, and trouble concentrating.34
MDMA affects many of the same neurotransmitter systems in the brain that are targeted by other addictive drugs. Experiments have shown that animals prefer MDMA, much like they do cocaine, over other pleasurable stimuli, another hallmark of most addictive drugs.35
|

|
|