
 |
 |
| |
National
Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
Division of Epidemiology and Prevention
Research
Alcohol Epidemiologic Data System
SURVEILLANCE REPORT #76
TRENDS IN ALCOHOL-RELATED FATAL
TRAFFIC CRASHES, UNITED STATES, 1982–2004
Hsiao-ye
Yi, Ph.D.
Chiung M. Chen, M.A.
Gerald D. Williams, D.Ed.
CSR,
Incorporated1
Suite 1000
2107 Wilson Boulevard
Arlington,
VA 22201
August 2006
U.S. Department
of Health and Human Services
Public Health Service
National Institutes
of Health
1 CSR, Incorporated, operates the Alcohol Epidemiologic Data System (AEDS) under Contract No. N01AA32007 for the Division of Epidemiology and Prevention Research, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). Dr. Rosalind A. Breslow serves as NIAAA Project Officer on the contract and oversaw the preparation of this report.
This is the 21st annual surveillance report from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) on trends in alcohol-related fatal traffic crashes. Data in this series of reports are compiled by the Alcohol Epidemiologic Data System (AEDS) from sources provided by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), the Federal Highway Administration (FHA), and the U.S. Census Bureau.
Beginning with the current report, AEDS implemented major methodological changes in determining alcohol involvement of fatal traffic crashes. This includes using imputed data on blood alcohol concentration (BAC) for drivers who were not tested for BAC or whose test results are unknown. The imputed BAC data are provided by NHTSA for 1982 and later years. In order to present consistent trend data, AEDS recalculated all historical numbers with the imputed BAC data and excluded data before 1982 from this report. As a result, the proportion of alcohol-related traffic crash fatalities as well as the proportion of drivers’ alcohol involvement in these crashes increased substantially from data presented in the previous issues of this report. Details of the methodological changes are discussed under the “Methods” section on Page 2. The following are highlights from the current report with the latest data for 2004:
Alcohol-Related Traffic Crash Fatalities
In 2004, about 16,919 persons died in alcohol-related traffic crashes, which constituted 39.5 percent of the total traffic crash fatalities.
The number of alcohol-involved drivers in fatal traffic crashes was 11,838 for male drivers and 2,286 for female drivers. These numbers represent about 28.0 and 14.9 percent of the total male and female drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes, respectively.
Alcohol-related traffic crash fatalities per 100 million vehicle miles traveled, 100,000 registered vehicles, 100,000 licensed drivers, and 100,000 population, were 0.57, 6.96, 8.51, and 5.76, respectively.
The proportion of alcohol-related traffic fatalities varied across States, ranging from 25.5 percent (Utah) to 52.2 percent (Rhode Island).
Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) Testing and Results
In 2004, the BAC testing rate for drivers killed in traffic crashes for the nation as a whole was 74.3 percent. The rate varied widely across States, ranging from 37.6 percent (Iowa) to 99.6 percent (North Carolina). The BAC testing rate generally remained low for surviving drivers (31.2 percent for the nation as a whole).
The percentage distribution of BAC values peaked at 0.10–0.14 grams per deciliter (g/dl) for drivers under age 21 and at 0.15–0.19 g/dl for all other age groups.
About 78 percent of drivers with positive BAC results had BAC scores of 0.10 g/dl or higher at the time of their crashes. If the legal BAC limit were lowered to 0.08 in all States, a total of 85 percent of the BAC-positive drivers would have been considered legally intoxicated.
Young Drinking Drivers
In 2004, about 22.5 percent of young drivers under age 21 in fatal traffic crashes were involved with alcohol, which is slightly lower than that for drivers ages 21 and older (24.8 percent).
Young drivers ages 21 to 24 continued to have the highest proportion (39.1 percent) of alcohol involvement among drivers in all age groups.
Trends in Alcohol-Related Fatal Traffic Crashes
The proportion of alcohol-related traffic fatalities declined from 59.6 percent in 1982 to 39.5 percent in 2004.
Drivers’ alcohol-involvement in fatal traffic crashes declined from 40.7 to 24.5 percent between 1982 and 2004. The decline was greater for drivers under age 21 (from 43.7 to 22.5 percent) than for drivers ages 21 and older (from 39.9 to 24.8 percent).
The BAC testing rate increased from 65.0 to 74.3 percent for drivers killed in fatal traffic crashes during 1982–2004. For surviving drivers, the rate increased from 22.0 to 31.2 percent.
One of the Healthy People 2010 objectives is to reduce alcohol-related motor vehicle crash deaths to 4.8 per 100,000 population. To achieve this goal, the rate must decrease by 17 percent from 2005 through 2010.
This 21st issue of the surveillance report on alcohol-related1 fatal traffic crashes is one in a series of surveillance reports prepared by NIAAA’s Alcohol Epidemiologic Data System (AEDS). These reports are designed to provide useful data to researchers, planners, policymakers, and other professionals interested in alcohol abuse and its associated illnesses and mortality.
(1 The terms “alcohol-related” and “alcohol-involved” are used interchangeably throughout this report.)
The 2004 mortality statistics show that “accidents (unintentional injuries)” were the number one cause of death for persons in the age groups of 1 to 4, 5 to 14, 15 to 24, and 25 to 44 in the United States; motor vehicle accident fatalities represented 39, 62, 72, and 47 percent of the deaths in this category for the four age groups, respectively. Overall, this category was the fifth leading cause of death in the United States in 2004; 40 percent of these deaths were due to motor vehicle accidents (Miniño, Heron, and Smith 2006). From 1982 through 2004 more than 40,000 people per year died in traffic crashes.
The Surgeon
General’s Workshop on Drunk Driving (Office of the Surgeon General 1989)
emphasized the need for accurate and timely epidemiologic data to address the
Nation’s drinking and driving problem. Data in this report are focused on
general trends in alcohol-related traffic fatalities, BAC testing rates and results,
and young drinking drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes.
The U.S. Department of Transportation’s Fatality Analysis Reporting System (FARS) is the major data source for this report. FARS contains data on all traffic crashes within the United States involving a motor vehicle traveling on a trafficway customarily open to the public and resulting in the death of a vehicle occupant or nonmotorist within 30 days of the crash. The system is operated by NHTSA in cooperation with each State. FARS collects detailed data on the conditions of a crash, the vehicle(s) involved, and the driver(s) and other person(s) involved. These data are obtained from each State’s existing documents (e.g., police accident reports, death certificates, and hospital medical records).
Denominators used in calculating fatality rates are taken from the following sources:
Resident population estimates as of July 1 of each year—provided by the U.S. Census Bureau (2000, 2002, 2006).
Numbers of registered vehicles, licensed drivers, and vehicle miles traveled—provided in the Highway Statistics series compiled annually by FHA (1983–2005).
Determination of Alcohol Involvement
Beginning with this issue, AEDS implemented two major methodological changes in determining alcohol involvement of fatal traffic crashes.
As a result of these changes, the estimated alcohol-related traffic crash fatalities as well as the number of alcohol-involved drivers increased substantially from data presented in previous issues of this report. For instance, compared with the earlier estimates for alcohol-related traffic fatalities, the new estimates increased by 20 to 40 percent for different years during 1982–2004.
In order to present consistent trend data, AEDS recalculated all historical numbers with these methodological changes and excluded data before 1982 from this report.
Fatality Measures
In this report, a fatality is considered to be alcohol-related if the death occurs as the result of an alcohol-related crash. Frequencies and percentage distributions of total and/or alcohol-related crash fatalities are calculated according to sex, age group, role in the crash (i.e., driver, passenger, or nonoccupant), and State, and presented in graphic and tabular form. In addition, the report includes rates based on associated risk factors.
The probability of having or being involved in a traffic crash depends on several factors (e.g., the amount of time a person spends on the road, the number of miles driven, vehicle speed, or type of vehicle driven). Four associated “risk factors”—vehicle miles traveled (VMT), the number of people in the population, the number of registered vehicles, and the number of licensed drivers—are used to express traffic crash fatalities as rates per these denominators. These rates place the raw frequencies within a context of associated risk factors, each of which is subject to change over time.
Finally, years of potential life lost (YPLL) are used to measure premature deaths due to traffic crashes. In this issue of the report, YPLL is calculated by subtracting the age at death from age 75 for each death (for decedents under age 75 only) and then accumulating the total across all deaths. This is a change from previous issues of this report, where YPLL was presented for persons under age 65. This change follows the change made in recent editions of the Health, United States series published by NCHS (2005), as the average life expectancy in the United States is over 75 years.
Trend data presentation
Most data are presented for all years from 1982 to the latest data year. For more detailed distributions (e.g., by State or detailed age groups), data are presented for only two years, 1998 and the latest data year. This is an effort to make the comparisons more relevant to observing current trends, as 1998 was used as the baseline year by Healthy People 2010 (CDC, 2006) for setting the target for reducing alcohol-related traffic fatalities.
Limitations
Although multiple imputation is an advanced methodology for missing data imputation, the imputed BAC values are subject to estimation errors. It is possible to calculate standard errors (or confidence intervals) for each estimate based on the multiply-imputed data (ten sets of values) for cases with missing BAC values. However, these data are not included in the report as the standard errors are generally small (e.g., less than 1 percent of the estimates for the total proportion of alcohol-involved fatal crashes), and presenting them would be overwhelming to most readers. Therefore readers are cautioned when making interpretations for small differences.
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Data 2010: The Healthy People 2010 Database (http://wonder.cdc.gov/data2010/, accessed August 2006)
Federal Highway Administration (FHA). Highway Statistics series 1982–2004. Washington, DC: Department of Transportation, 1983–2005.
Miniño, A.M.; Heron, M.P.; and Smith, B.L. Deaths: Preliminary data for 2004. National Vital Statistics Reports 54(19). Hyattsville, Maryland: National Center for Health Statistics, 2006.
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). Health, United States, 2005, With Chartbook on Trends in Health of Americans. Hyattsville, Maryland: 2005.
National Highway Transportation Safety Administration (NHTSA). Transitioning to Multiple Imputation—A New Method to Impute Missing Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) Values in FARS. NHTSA Technical Report, DOT HS 809 403. Washington, DC: Department of Transportation, 2002.
Office of the Surgeon General. Surgeon General’s Workshop on Drunk Driving. Proceedings. Washington, DC: December 14–16, 1988. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1989.
U.S. Census Bureau. U.S. Population Estimates by Age, Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin: 1980 to 1999. Release date: April 11, 2000.
U.S. Census Bureau. Intercensal Estimates of the United States Resident Population by Age Groups and Sex, 1990–2000: Selected Month (US-EST90INT-07). Release date: September 13, 2002.
U.S. Census Bureau. Annual Estimates of the Population by Sex and Five-Year Age Groups for the United States: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2005 (NCEST2005- 01). Release Date: May 10, 2006.
Figure 1. Alcohol-related and nonalcohol-related traffic crash fatalities, United States, 1982–2004.
Figure 2a. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100 million vehicle miles traveled (VMT), United States, 1982–2004.
Figure 2b. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100,000 registered vehicles, United States, 1982–2004.
Figure 2c. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100,000 licensed drivers, United States, 1982–2004.
Figure 2d. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100,000 population, United States, 1982–2004.
Figure 3a. Decedent’s role in nonalcohol-related traffic fatalities, United States, 2004.
Figure 3b. Decedent’s role in alcohol-related traffic fatalities, United States, 2004.
Figure 4. Percentage of drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes and given BAC tests, according to injury severity, United States, 1982–2004.
Figure 5. Percentage distributions of BAC among alcohol-involved drivers, according to age, United States, 2004.
Figure 6. Percentage of alcohol involvement among drivers in fatal traffic crashes, according to age, United States, 1998 and 2004.
Figure 7. Percentage of alcohol involvement among young drivers under age 21 and drivers ages 21 and older in fatal traffic crashes, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 1. Traffic crashes, traffic crash fatalities, and alcohol-related traffic crash fatalities, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 2. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100 million vehicle miles traveled and 100,000 registered vehicles, licensed drivers, and population, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 3. Years of potential life lost (YPLL) from total and alcohol-related traffic crashes, according to sex, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 4. Alcohol-related traffic crash fatalities, according to age, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 5. Total and alcohol-related traffic crash fatalities according to decedent’s role, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 6. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatalities according to State, United States, 1998 and 2004.
Table 7. Drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes, according to sex and alcohol involvement, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 8. Drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes and given blood alcohol concentration (BAC) tests, according to injury severity, United States, 1982–2004.
Table 9. Drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes and given blood alcohol concentration (BAC) tests, according to State and injury severity, United States, 1998 and 2004.
Table 10. Drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes and given blood alcohol concentration (BAC) tests, according to sex, age, and injury severity, United States, 1998 and 2004.
Table 11. Percentage distributions of blood alcohol concentration (BAC) level among alcohol-involved drivers, according to sex and age, United States, 1998 and 2004.
Table 12. Driver’s alcohol involvement in fatal traffic crashes, according to sex and age, United States, 1998 and 2004.
Table 13. Alcohol involvement among young drivers under age 21 and drivers ages 21 and older in fatal traffic crashes, United States, 1982–2004.
Figure 1. Alcohol-related and nonalcohol-related traffic crash fatalities, United States, 1982–2004.
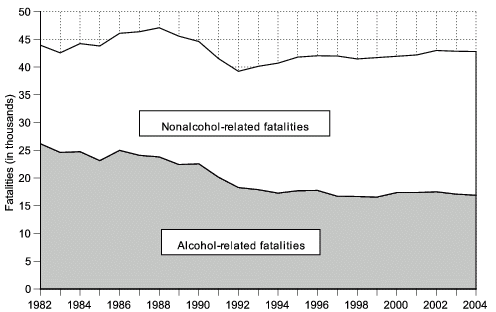
Data for figure 1 are presented in Table 1.
Figure 2a. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100 million vehicle miles traveled (VMT), United States, 1982–2004.
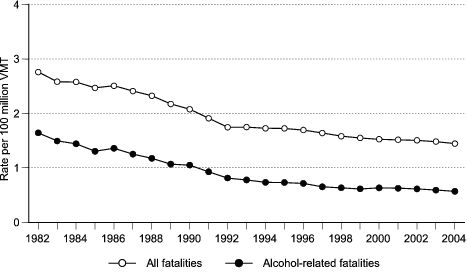
Data for figure 2a are presented in Table 2.
Figure 2b. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100,000 registered vehicles, United States, 1982–2004.
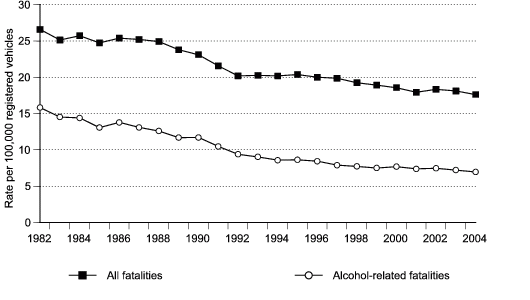
Data for figure 2b are presented in Table 2.
Figure 2c. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100,000 licensed drivers, United States, 1982–2004.
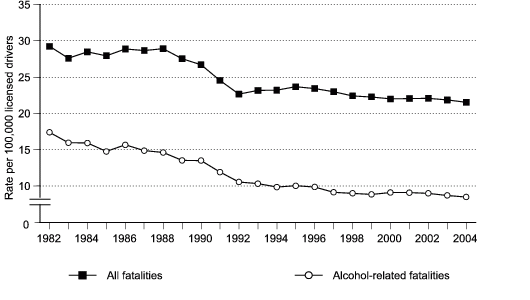
Data for figure 2c are presented in Table 2.
Figure 2d. Total and alcohol-related traffic fatality rates per 100,000 population, United States, 1982–2004.
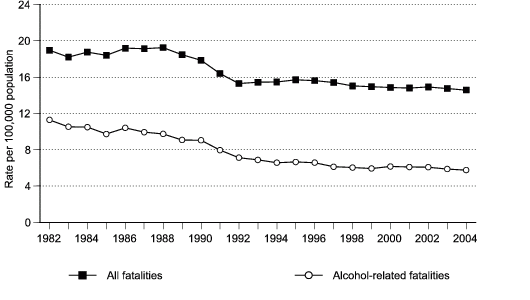
Data for figure 2d are presented in Table 2.
Figure 3a. Decedent’s role in nonalcohol-related traffic fatalities, United States, 2004.
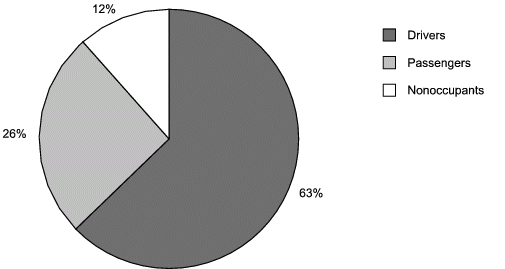 d
d
Note: 45 decedents were excluded from this pie chart because their roles were
unknown.
Figure 3b. Decedent’s role in alcohol-related traffic fatalities, United States, 2004.
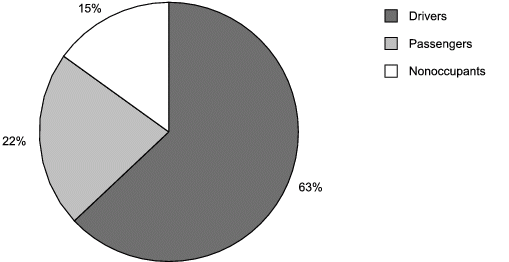 d
d
Note: 33 decedents were excluded from this pie chart because their roles were
unknown.
Figure 4. Percentage of drivers involved in fatal traffic crashes and given BAC tests, according to injury severity, United States, 1982–2004.
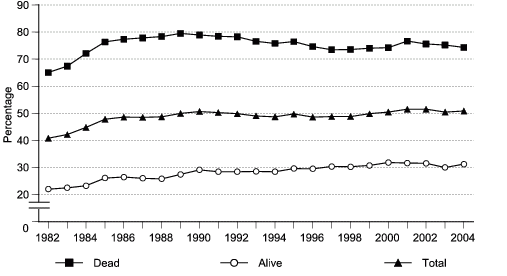
Data for figure 4 are presented in Table 8.
Figure 5. Percentage distributions of BAC among alcohol-involved drivers, according to age, United States, 2004.
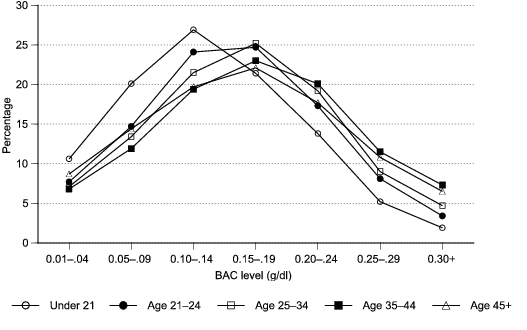
Data for figure 5 are presented in Table 11.
Figure 6. Percentage of alcohol involvement among drivers in fatal traffic crashes, according to age, United States, 1998 and 2004.
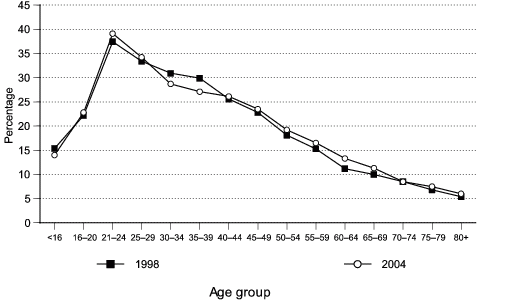
Data for figure 6 are presented in Table 12.
Figure 7. Percentage of alcohol involvement among young drivers under age 21 and drivers ages 21 and older in fatal traffic crashes, United States, 1982–2004.
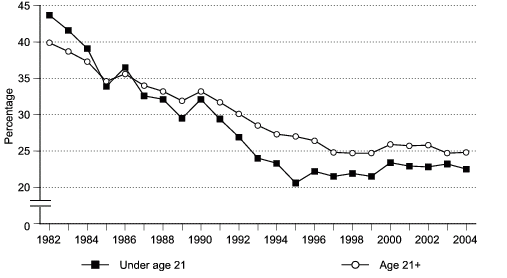
Data for figure 7 are presented in Table 13.
| ||||||||||||||