| Assessment of Regional Cytochrome P450 Activities in Rat Liver Slices Using Resorufin Substrates and Fluorescence Confocal Laser Cytometry
John T. Heinonen, Jaspreet S. Sidhu, Maureen T. Reilly, Federico M. Farin, Curtis J. Omiecinski, David L. Eaton, and Terrance J. Kavanagh Department of Environmental Health, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195 USA Abstract
Characterizing constitutive activities and inducibility of various cytochrome P450 isozymes is important for elucidating species and individual differences in susceptibility to many toxicants. Although expression of certain P450s has been studied in homogenized tissues, the ability to assess functional enzyme activity without tissue disruption would further our understanding of interactive factors that modulate P450 activities. We used precision-cut, viable rat liver slices and confocal laser cytometry to determine the regional enzyme activities of P450 isozymes in situ. Livers from control and ß-naphthoflavone (ßNF) -treated rats were sectioned with a Krumdieck tissue slicer into 250-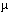 m thick sections. A slice perfusion chamber that mounts on the cytometer stage was developed to allow for successive measurement of region-specific P450-dependent O-dealkylation of 7-ethoxy-, 7-pentoxy-, and 7-benzyloxyresorufin (EROD, PROD, and BROD activity, respectively) in the same liver slice. Images of the accumulated fluorescent resorufin product within the tissue were acquired using a confocal laser cytometer in confocal mode. As expected, slices isolated from ßNF-treated rats showed high levels of centrilobular EROD activity compared to slices from control rats, whereas PROD and BROD activities remained at control levels. These techniques should allow for the accurate quantification of regional and cell-specific P450 enzyme activity and, with subsequent analysis of the same slice, the ability to correlate specific P450 mRNAs or other factors with enzymatic activity. Moreover, these techniques should be amenable to examination of similar phenomena in other tissues such as lung and kidney, where marked heterogeneity in cellular P450 expression patterns is also known to occur. Key words: cytochrome P450, hepatic zones, laser cytometry, liver slices, regional activity. Environ Health Perspect 104:536-543 (1996) m thick sections. A slice perfusion chamber that mounts on the cytometer stage was developed to allow for successive measurement of region-specific P450-dependent O-dealkylation of 7-ethoxy-, 7-pentoxy-, and 7-benzyloxyresorufin (EROD, PROD, and BROD activity, respectively) in the same liver slice. Images of the accumulated fluorescent resorufin product within the tissue were acquired using a confocal laser cytometer in confocal mode. As expected, slices isolated from ßNF-treated rats showed high levels of centrilobular EROD activity compared to slices from control rats, whereas PROD and BROD activities remained at control levels. These techniques should allow for the accurate quantification of regional and cell-specific P450 enzyme activity and, with subsequent analysis of the same slice, the ability to correlate specific P450 mRNAs or other factors with enzymatic activity. Moreover, these techniques should be amenable to examination of similar phenomena in other tissues such as lung and kidney, where marked heterogeneity in cellular P450 expression patterns is also known to occur. Key words: cytochrome P450, hepatic zones, laser cytometry, liver slices, regional activity. Environ Health Perspect 104:536-543 (1996) Address correspondence to T. J. Kavanagh, Department of Environmental Health, Box 354695, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195 USA. We thank Chen-Ye He for preparing the liver sections used in immunocytochemical staining and Mark Cooper of the Department of Zoology at the University of Washington for helpful discussions on the design of the perfusion chamber. This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants ES-04696, ES-05780, ES-04616, and ES-03933) . Received 24 March 1995 ; accepted 18 January 1996.
The full version of this article is available for free in HTML format. |

