|
|
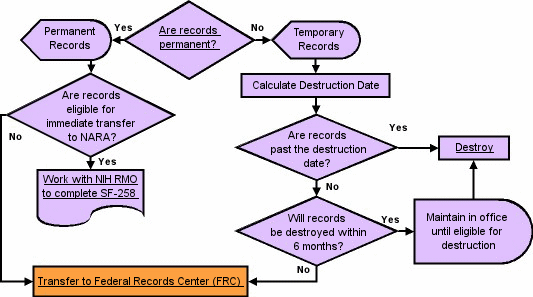
NIH Manual Chapter 1743, Keeping and Destroying Records contains descriptions of records series. It also provides you with specific instructions as to how long records may be kept and what must be done with them after the specified period. These instructions are known as the disposition, and this information is provided at the end of each series description. After you identify the records series, a disposition date can be calculated. Records can be either temporary or permanent. Temporary records are those records that the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) approves for either immediate disposal or for disposal after a specified time or event. Temporary records not yet at their destruction date, depending on how long they must be held, can be handled in two ways:
Permanent records are those that NARA identifies as having sufficient value to warrant continued preservation by the federal government as part of the National Archives of the United States. Permanent records can also be handled in two ways:
Records transferred to storage may be sent to a federal records center (FRC) or a commercial storage facility. The use of an FRC is recommended. These facilities actively manage your records and will guide you every step of the way. FRCs offer pickup and delivery services in the Washington, DC, area, alert you when your records have reached their destruction date, handle the transfer of records to NARA, and provide reference services for easy access to your records. You may choose to store your records at commercial storage facilities; however, the facility must meet NARA regulations. If records are past their destruction date and they are not subject to a records audit, freeze, or other event that may forbid it, they should be immediately destroyed. If more than six months remain until the records become eligible for destruction, you should transfer them to an FRC for storage. If less than six months remain until the destruction date, you may temporarily maintain the records in your office. The National Interagency Fire Center website provides a useful tool which calculates the disposition date according to NARA’s quarterly disposition schedule. Examples of dispositions found in 1743 include:
These instructions are used to calculate the records' date of final action. Below are links to examples of calculating final action dates:
|
 |
National Institutes of Health
|

|