Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR)
The two key markers for kidney disease are urine albumin and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
For patients with type 1 diabetes for 5 years or more or with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association and the National Kidney Disease Education Program (NKDEP) recommend that health care professionals:
- Assess urine albumin excretion yearly to diagnose and monitor kidney damage. More frequent monitoring may be indicated in patients with changing clinical status or after therapeutic interventions.
- Screen using a spot UACR. UACR estimates 24-hour urine albumin excretion. 24-hour collection and timed specimens are not necessary.
Reducing urine albumin to the normal or near-normal range may improve renal and cardiovascular prognoses.
| Urine Albumin (mg/dL) |
= UACR in mg/g ≈ Albumin excretion in mg/day |
 |
| Urine Creatinine (g/dL) |
UACR is a ratio between two measured substances. Unlike a dipstick test for albumin, it is unaffected by variation in urine concentration. |
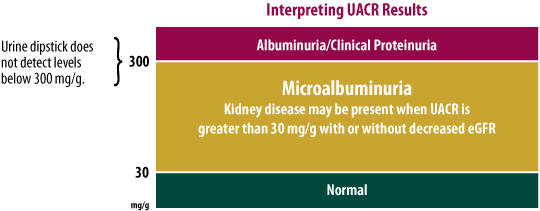
If kidney disease is detected, it should be addressed as part of a comprehensive approach to the
treatment of diabetes.
|
Estimated GFR
The two key markers for kidney disease are eGFR and urine albumin.
The American Diabetes Association and NKDEP recommend that health care professionals:
- Calculate eGFR from stable serum creatinine levels at least once a year in all patients with diabetes.
| — |
eGFR is more accurate than serum creatinine alone. Serum creatinine is affected by muscle mass, and related factors of age, sex, and race.
|
| — |
eGFR is not reliable for patients with normal kidney function, rapidly changing creatinine levels, or extremes in muscle mass and diet, e.g., very muscular or large people, cachectic people, and vegans.
|
See if your lab reports eGFR routinely or if you need to request it. GFR calculators are available on NKDEP's website at www.nkdep.nih.gov/professionals/gfr_calculators.
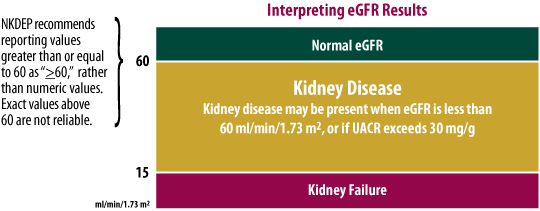
If kidney disease is detected, it should be addressed as part of a comprehensive approach to the
treatment of diabetes.
|