| Expression of Xenobiotic-Metabolizing Enzymes in Cultured Rat Tracheal Epithelial Cells Andre Castonguay,1 Lila Overby, Paul Nettesheim,2 George C. Clark,2 and Richard M. Philpot2 1School of Pharmacy, Laval University, Quebec City, GIK 794 Canada
2National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, Research Triangle Park, NC 27606 USA Abstract
Rat tracheal epithelial (RTE) cells were cultured on membrane support with and without retinoic acid (RA) . In early (6-day-old) cultures, the epithelium is a monolayer or bilayer of undifferentiated cells and secretes little mucuslike product either in the absence or presence of RA. In late (12- to 15-day-old) cultures, the epithelium differentiates as a mucociliary epithelium in the presence of RA and as a squamous epithelium in the absence of RA. The purpose of our study was to determine whether a number of xenobiotic enzymes are expressed in these cultures and whether their expression depends on the state of differentiation. Enzyme expression was characterized by electrophoresis and immunoblotting as a function of time in culture and phenotypic differentiation. Cytochrome P450 1A1 was not expressed in freshly harvested RTE cells. This isoenzyme was induced in rats by gavage with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) or by exposure of early RTE cell cultures to TCDD, provided RA was also added to the cultures. Cytochrome P450 2B1 was observed in freshly isolated RTE cells, but not in early or late RTE cultures. In contrast, expression of NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase was decreased in early cultures, but was increased in well-differentiated cultures. Flavin-containing monooxygenase was detected in lung tissue, but not in freshly harvested or cultured RTE cells. Glutathione S-transferases (GST) µ and 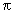 were expressed in freshly harvested RTE cells. GST were expressed in freshly harvested RTE cells. GST  was expressed in early and late cultures, whereas GST µ was expressed in late cultures, but could not be found in early cultured RTE cells. Levels of GST isoenzymes were unaffected by RA. These results parallel the expression of enzymes observed in proliferating and differentiating epithelium induced by mechanical injury in vivo. Induction of monooxygenases by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons results in RTE cells with metabolic activating and deactivating enzymes and constitutes a system suited for some toxicological studies. Key words: cytochrome P450 , flavin-containing monooxygenase, glutathione transferase , mucin , rat tracheal cells , retinoic acid , TCDD. Environ Health Perspect 103: 254-258 (1995) was expressed in early and late cultures, whereas GST µ was expressed in late cultures, but could not be found in early cultured RTE cells. Levels of GST isoenzymes were unaffected by RA. These results parallel the expression of enzymes observed in proliferating and differentiating epithelium induced by mechanical injury in vivo. Induction of monooxygenases by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons results in RTE cells with metabolic activating and deactivating enzymes and constitutes a system suited for some toxicological studies. Key words: cytochrome P450 , flavin-containing monooxygenase, glutathione transferase , mucin , rat tracheal cells , retinoic acid , TCDD. Environ Health Perspect 103: 254-258 (1995) Address correspondence to A. Castonguay, Laboratory of Cancer Etiology and Chemoprevention, School of Pharmacy, Laval University, Québec City, G1K 7P4 Canada. This work was supported by NIEHS. We appreciate the technical assistance of Scott H. Randell in morphological studies of RTE cells and Veronica B. Godfrey with cell culture. Received 8 August 1994 ; accepted 13 December 1994.
The full version of this article is available for free in HTML format. |

