Early Childhood Professional Development Systems Toolkit
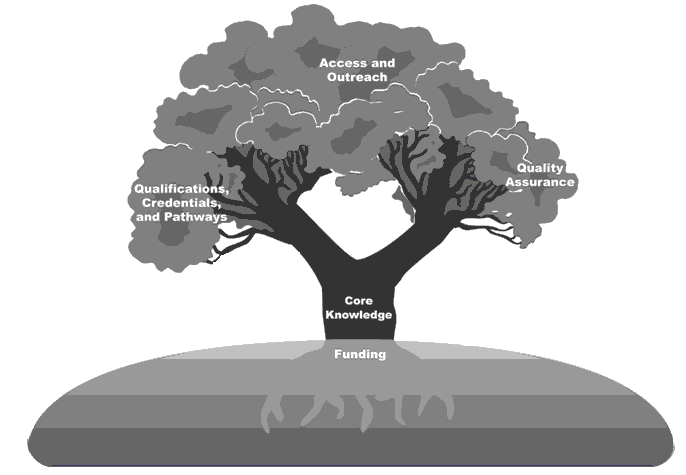 |
Like a tree, a professional development system is a dynamic arrangement of interdependent elements. The trunk of core knowledge provides the central foundation for the entire system. It upholds the quality assurance branch; the qualifications, credentials, and pathways branch; and the leaves of access and outreach, which extend to all sectors of the early care and education workforce. The roots of funding provide the essential monetary support for practitioners to attend professional development activities and be compensated for increased professional development.
Core Knowledge
- Core knowledge: The central concepts that adults who work with young children need to know and understand to facilitate children’s learning and development, which are linked to early learning guidelines.
- Core competencies: The central range of observable skills that adults who work with young children need to facilitate children’s learning and development, which are linked to early learning guidelines.
Access and Outreach
- Vision and mission statements, and guiding principles.
- Online databases of training and education opportunities.
- Training calendars: Published lists of trainings for personnel, which generally include short descriptions, locations, dates, and times of training sessions.
- Directories of college degree programs.
- Career development advising: The process of informing individuals about entry and continuing education requirements for professional roles in the field and helping them assess current qualifications, identify education resources, and plan career advancement, while paying attention to cultural and linguistic frameworks.
- Continuum of individual and group supports:
- Orientations to the early childhood field, regulations, standards, or programs.
- Mentoring and coaching programs.
- Peer support groups.
- Leadership development.
- General skills and education supports (e.g., bilingual education and literacy, computer, math skill building, etc.).
- Multiple professional development delivery methods:
- Onsite, community-based, and higher education/campus-based delivery.
- Mobile units.
- Distance learning.
- Courses as modularized workshops (i.e., credit-bearing courses that are developed into a set of related workshops).
- Internships, assistantships, and apprenticeships.
- Hotlines, warmlines, help desks.
- Technical assistance.
- Public engagement efforts/initiatives.
Qualifications, Credentials, and Pathways
- Preservice requirements: Minimum qualifications that staff are required to have prior to assuming their positions.
- Continuing education requirements: Ongoing trainings that staff are required to obtain to remain in their positions.
- Career lattice: Levels of mastery connected to a progression of roles in the field.
- Credentials: Documents certifying that an individual has met a defined set of requirements set forth by the grantor of the credential, usually related to skills and knowledge, and may include demonstrations of competence.
- Pathways leading to qualifications, degrees, and credentials:
- Articulation agreements.
- Training registries: Databases that track all completed personnel training.
- Credit-bearing workshops and training series.
- Credit for prior learning: Systems used by institutions of higher education for granting credit for learning acquired through life and/or work experiences.
Funding
- Financial aid and scholarships.
- Compensation/retention initiatives: Strategies for increasing compensation to retain qualified personnel, and linking increases in qualifications to increases in compensation.
- Program quality awards (these may be part of a quality rating system):
- Tiered reimbursement systems: Methods for increasing payment rates based on quality in the State or Territory’s child care subsidy system).
- Tiered quality rewards: Direct payments based on quality not tied to State/Territory child care subsidies.
Quality Assurance
- Approval processes:
- Trainer approval (i.e., standards and registries): Sets of standards and qualifications for those who offer training, or registries that track trainer qualifications and standards they have met.
- Training approval: Sets of standards that trainings must meet, usually linked to core knowledge and principles of adult learning.
- Evaluation processes: Built into each element and/or component and the overall system; an iterative process.
- Monitoring processes: Monitoring adherence to staff qualification and professional development requirements specified in licensing regulations, program or funding standards, accreditation, etc.
- Accreditation.


![Image of baby [NCCIC header image]](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20090109025645im_/http://nccic.acf.hhs.gov/assets/images/template/baby.jpg)
![Image of seven children, including school-age children and a toddler [NCCIC Header Image]](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20090109025645im_/http://nccic.acf.hhs.gov/assets/images/template/children_right.jpg)


