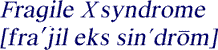|
defined: |
 |
After Down syndrome, the second most frequent genetic cause of mental retardation. The disorder is one of a group of diseases that results from an unusual kind of mutation: an expansion of a repeating sequence of three
letters of the DNA code, called a triplet repeat or trinucleotide repeat.
In Fragile X, the
repeating triplet is CGG, cytosine-guanine-guanine, in a gene called FMR1 on the X chromosome. There are ordinarily fewer than 55 copies of the repeat. When the number of repeats exceeds 200, the expansion is called a "full mutation" and expression of the
FMR1 gene is shut off, causing the fragile X syndrome.
Individuals who carry between 55 and 200 copies of the repeat, called a "premutation", may transmit a gene with a full mutation (>200 repeats) to their children, but are generally not affected
by the full-blown fragile X syndrome themselves.
Carriers of premutations may have difficulties with mild cognitive or behavioral problems, premature ovarian failure in female carriers,and an adult-onset neurological disorder
causing tremor and difficulties with balance and gait.
|