Guidance for Industry
Q3C - Tables and List
[PDF version of this document]

Additional copies are available from:
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER)
Division of Drug Information (HFD-240)
Food and Drug Administration
5600 Fishers Lane
Rockville, MD 20857
(Tel) 301-827-4573
http://www.fda.gov/cder/guidance/index.htm
or
Office of Communication, Training, and
Manufacturers Assistance (HFM-40)
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER)
Food and Drug Administration
1401 Rockville Pike
Rockville, MD 20852-1448
http://www.fda.gov/cber/guidelines.htm;
(Tel) Voice Information System at 800-835-4709 or 301-827-1800
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Food and Drug Administration
Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER)
Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER)
November 2003
ICH
Revision 1

Guidance for Industry1
Q3C - Tables and List
Contains Nonbinding Recommendations
| This guidance represents the Food and Drug Administration's (FDA's) current thinking on this topic. It does not create or confer any rights for or on any person and does not operate to bind FDA or the public. You can use an alternative approach if that approach satisfies the requirements of the applicable statutes and regulations. If you want to discuss an alternative approach, contact the FDA staff responsible for implementing this guidance. If you cannot identify the appropriate FDA staff, call the appropriate number listed on the title page of this guidance. |

- INTRODUCTION
This is the companion document for the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) guidance for industry Q3C Impurities: Residual Solvents (1997), which makes recommendations as to what amounts of residual solvents are considered safe in pharmaceuticals.
This document may be updated if proposals for change are submitted to the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Steering Committee. Proposals for change and the ICH Steering Committee final decision on any proposed changes will be announced through a notice in the Federal Register prior to the updating of this document.
FDA's guidance documents, including this guidance, do not establish legally enforceable responsibilities. Instead, guidances describe the Agency's current thinking on a topic and should be viewed only as recommendations, unless specific regulatory or statutory requirements are cited. The use of the word should in Agency guidances means that something is suggested or recommended, but not required.

- LIST OF SOLVENTS INCLUDED IN THE Q3C GUIDANCE
| Solvent |
Other Names |
Structure |
Class |
| |
|
|
|
| Acetic acid |
Ethanoic acid |
CH3COOH |
Class 3 |
| Acetone |
2-Propanone
Propan-2-one |
CH3COCH3 |
Class 3 |
| Acetonitrile |
|
CH3CN |
Class 2 |
| Anisole |
Methoxybenzene |
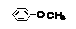 |
Class 3 |
| Benzene |
Benzol |
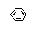 |
Class 1 |
| 1-Butanol |
n-Butyl alcohol
Butan-1-ol |
CH3(CH2)3OH |
Class 3 |
| 2-Butanol |
sec-Butyl alcohol
Butan-2-ol |
CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3 |
Class 3 |
| Butyl acetate |
Acetic acid butyl ester |
CH3COO(CH2)3CH3 |
Class 3 |
| tert-Butylmethyl ether |
2-Methoxy-2-methyl-propane |
(CH3)3COCH3 |
Class 3 |
| Carbon tetrachloride |
Tetrachloromethane |
CCl4 |
Class 1 |
| Chlorobenzene |
|
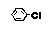 |
Class 2 |
| Chloroform |
Trichloromethane |
CHCl3 |
Class 2 |
| Cumene |
Isopropylbenzene
(1-Methyl)ethylbenzene |
C6H5-CH(CH3)2 |
Class 3 |
| Cyclohexane |
Hexamethylene |
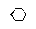 |
Class 2 |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane |
sym-Dichloroethane
Ethylene dichloride
Ethylene chloride |
CH2ClCH2Cl |
Class 1 |
| 1,1-Dichloroethene |
1,1-Dichloroethylene
Vinylidene chloride |
H2C=CCl2 |
Class 1 |
| 1,2-Dichloroethene |
1,2-Dichloroethylene
Acetylene dichloride |
ClHC=CHCl |
Class 2 |
| Dichloromethane |
Methylene chloride |
CH2Cl2 |
Class 2 |
| 1,2-Dimethoxyethane |
Ethyleneglycol dimethyl ether
Monoglyme
Dimethyl Cellosolve |
H3COCH2CH2OCH3 |
Class 2 |
N,N-
Dimethylacetamide |
DMA |
CH3CON(CH3)2
| Class 2 |
| N,N- Dimethylformamide |
DMF |
HCON(CH3)2 |
Class 2 |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide |
Methylsulfinylmethane
Methyl sulfoxide
DMSO |
(CH3)2SO |
Class 3 |
| 1,4-Dioxane |
p-Dioxane
[1,4]Dioxane |
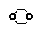
| Class 2 |
| Ethanol |
Ethyl alcohol |
CH3CH2OH |
Class 3 |
| 2-Ethoxyethanol |
Cellosolve |
CH3CH2OCH2CH2OH |
Class 3 |
| Ethyl acetate |
Acetic acid ethyl ester |
CH3COOCH2CH3 |
Class 3 |
| Ethyleneglycol |
1,2-Dihydroxyethane
1,2-Ethanediol |
HOCH2CH2OH |
Class 2 |
| Ethyl ether |
Diethyl ether
Ethoxyethane
1,1'-Oxybisethane |
CH3CH2OCH2CH3 |
Class 3 |
| Ethyl formate |
Formic acid ethyl ester |
HCOOCH2CH3 |
Class 3 |
| Formamide |
Methanamide |
HCONH2 |
Class 2 |
| Formic acid |
|
HCOOH |
Class 3 |
| Heptane |
n-Heptane |
CH3(CH2)5CH3 |
Class 3 |
| Hexane |
n-Hexane |
CH3(CH2)4CH3 |
Class 2 |
| Isobutyl acetate |
Acetic acid isobutyl ester |
CH3COOCH2CH(CH3)2 |
Class 3 |
| Isopropyl acetate |
Acetic acid isopropyl ester |
CH3COOCH(CH3)2 |
Class 3 |
| Methanol |
Methyl alcohol |
CH3OH |
Class 2 |
| 2-Methoxyethanol |
Methyl Cellosolve |
CH3OCH2CH2OH |
Class 2 |
| Methyl acetate |
Acetic acid methyl ester |
CH3COOCH3 |
Class 3 |
| 3-Methyl-1-butanol |
Isoamyl alcohol
Isopentyl alcohol
3-Methylbutan-1-ol |
(CH3)2CHCH2CH2OH |
Class 3 |
| Methylbutyl ketone |
2-Hexanone
Hexan-2-one |
CH3(CH2)3COCH3 |
Class 2 |
| Methylcyclohexane |
Cyclohexylmethane |
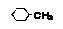 |
Class 2 |
| Methylethyl ketone |
2-Butanone
MEK
Butan-2-one |
CH3CH2COCH3 |
Class 3 |
| Methylisobutyl ketone |
4-Methylpentan-2-one
4-Methyl-2-pentanone
MIBK |
CH3COCH2CH(CH3)2 |
Class 3 |
| 2-Methyl-1-propanol |
Isobutyl alcohol
2-Methylpropan-1-ol |
(CH3)2CHCH2OH |
Class 3 |
| N-Methylpyrrolidone |
1-Methylpyrrolidin-2-one
1-Methyl-2-pyrrolidinone |
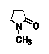 |
Class 2 |
| Nitromethane |
|
CH3NO2 |
Class 2 |
| Pentane |
n-Pentane |
CH3(CH2)3CH3 |
Class 3 |
| 1-Pentanol |
Amyl alcohol
Pentan-1-ol
Pentyl alcohol |
CH3(CH2)3CH2OH |
Class 3 |
| 1-Propanol |
Propan-1-ol
Propyl alcohol |
CH3CH2CH2OH |
Class 3 |
| 2-Propanol |
Propan-2-ol
Isopropyl alcohol |
(CH3)2CHOH |
Class 3 |
| Propyl acetate |
Acetic acid propyl ester |
CH3COOCH2CH2CH3 |
Class 3 |
| Pyridine |
|
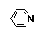 |
Class 2 |
| Sulfolane |
Tetrahydrothiophene 1,1-dioxide |
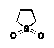 |
Class 2 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
Tetramethylene oxide
Oxacyclopentane |
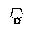 |
Class 2 |
| Tetralin |
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-naphthalene |
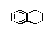 |
Class 2 |
| Toluene |
Methylbenzene |
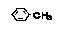 |
Class 2 |
| 1,1,1-Trichloroethane |
Methylchloroform |
CH3CCl3 |
Class 1 |
| 1,1,2-Trichloroethene |
Trichloroethene |
HClC=CCl2 |
Class 2 |
| Xylene1 |
Dimethybenzene
Xylol |
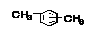 |
Class 2 |
1Usually 60% m-xylene, 14% p-xylene, 9% o-xylene with 17% ethyl benzene.

- SOLVENTS GROUPED BY CLASS
Solvents in Class 1 (Table 1) should not be employed in the manufacture of drug substances, excipients, and drug products because of their unacceptable toxicity or their deleterious environmental effect. However, if their use is unavoidable in order to produce a drug product with a significant therapeutic advance, then their levels should be restricted as shown in Table 1, unless otherwise justified. The solvent 1,1,1-Trichloroethane is included in Table 1 because it is an environmental hazard. The stated limit of 1,500 ppm is based on a review of the safety data.
Table 1. - Class 1 Solvents in Pharmaceutical Products (Solvents That Should Be Avoided)
| Solvent |
Concentration Limit
(ppm) |
Concern |
| |
|
|
| Benzene |
2 |
Carcinogen |
| Carbon tetrachloride |
4 |
Toxic and environmental hazard |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane |
5 |
Toxic |
| 1,1-Dichloroethene |
8 |
Toxic |
| 1,1,1-Trichloroethane |
1,500 |
Environmental hazard |
Solvents in Class 2 (Table 2) should be limited in pharmaceutical products because of their inherent toxicity. PDEs are given to the nearest 0.1 mg/day, and concentrations are given to the nearest 10 ppm. The stated values do not reflect the necessary analytical precision of determination. Precision should be determined as part of the validation of the method.
Table 2. - Class 2 Solvents in Pharmaceutical Products
| Solvent |
PDE (mg/day) |
Concentration Limit (ppm) |
| |
|
|
| Acetonitrile |
4.1 |
410 |
| Chlorobenzene |
3.6 |
360 |
| Chloroform |
0.6 |
60 |
| Cyclohexane |
38.8 |
3,880 |
| 1,2-Dichloroethene |
18.7 |
1,870 |
| Dichloromethane |
6.0 |
600 |
| 1,2-Dimethoxyethane |
1.0 |
100 |
| N,N-Dimethylacetamide |
10.9 |
1,090 |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide |
8.8 |
880 |
| 1,4-Dioxane |
3.8 |
380 |
| 2-Ethoxyethanol |
1.6 |
160 |
| Ethyleneglycol |
6.2 |
620 |
| Formamide |
2.2 |
220 |
| Hexane |
2.9 |
290 |
| Methanol |
30.0 |
3,000 |
| 2-Methoxyethanol |
0.5 |
50 |
| Methylbutyl ketone |
0.5 |
50 |
| Methylcyclohexane |
11.8 |
1,180 |
| N-Methylpyrrolidone |
5.3 |
530 |
| Nitromethane |
0.5 |
50 |
| Pyridine |
2.0 |
200 |
| Sulfolane |
1.6 |
160 |
| Tetrahydrofuran |
7.2 |
720 |
| Tetralin |
1.0 |
100 |
| Toluene |
8.9 |
890 |
| 1,1,2-Trichloroethene |
0.8 |
80 |
| Xylene1 |
21.7 |
2,170 |
1Usually 60% m-xylene, 14% p-xylene, 9% o-xylene with 17% ethyl benzene.
Solvents in Class 3 (Table 3) may be regarded as less toxic and of lower risk to human health. Class 3 includes no solvent known as a human health hazard at levels normally accepted in pharmaceuticals. However, there are no long-term toxicity or carcinogenicity studies for many of the solvents in Class 3. Available data indicate that they are less toxic in acute or short-term studies and negative in genotoxicity studies. It is considered that amounts of these residual solvents of 50 mg per day or less (corresponding to 5,000 ppm or 0.5 percent under Option 1) would be acceptable without justification. Higher amounts may also be acceptable provided they are realistic in relation to manufacturing capability and good manufacturing practice (GMP).
Table 3. - Class 3 Solvents Which Should Be Limited by GMP or Other Quality-Based Requirements
| Acetic acid |
Heptane |
| Acetone |
Isobutyl acetate |
| Anisole |
Isopropyl acetate |
| 1-Butanol |
Methyl acetate |
| 2-Butanol |
3-Methyl-1-butanol |
| Butyl acetate |
Methylethyl ketone |
| tert-Butylmethyl ether |
Methylisobutyl ketone |
| Cumene |
2-Methyl-1-propanol |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide |
Pentanel |
| Ethanol |
1-Pentanol |
| Ethyl acetate |
1-Propanol |
| Ethyl ether |
2-Propanol |
| Ethyl formate |
Propyl acetate |
| Formic acid |
|
The solvents listed in Table 4 may also be of interest to manufacturers of excipients, drug substances, or drug products. However, no adequate toxicological data on which to base a PDE were found. Manufacturers should supply justification for residual levels of these solvents in pharmaceutical products.
Table 4. - Solvents for Which No Adequate Toxicological Data Were Found
| 1,1-Diethoxypropane |
Methylisopropyl ketone |
| 1,1-Dimethoxymethane |
Methyltetrahydrofuran |
| 2,2-Dimethoxypropane |
Petroleum ether |
| Isooctane |
Trichloroacetic acid |
| Isopropyl ether |
Trifluoroacetic acid |

1
This document was developed within the Expert Working Group (Quality) of the International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) and has been subject to consultation by the regulatory parties, in accordance with the ICH process. This document was endorsed by the ICH Steering Committee at Step 4 of the ICH process in July 1997. At Step 4 of the process, the final draft is recommended for adoption to the regulatory bodies of the European Union, Japan, and the United States. This guidance was published in the Federal Register on December 24, 1997 (62 FR67377), and is applicable to drug and biological products.
|




