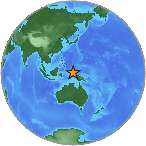
Magnitude 7.4 - NEAR THE NORTH COAST OF PAPUA, INDONESIA
2009 January 03 22:33:40 UTC
Earthquake Details
| Magnitude | 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Date-Time |
|
| Location | 0.707°S, 133.361°E |
| Depth | 23 km (14.3 miles) set by location program |
| Region | NEAR THE NORTH COAST OF PAPUA, INDONESIA |
| Distances | 85 km (55 miles) WNW of Manokwari, Papua, Indonesia 230 km (140 miles) E of Sorong, Papua, Indonesia 1335 km (820 miles) NNE of DARWIN, Northern Territory, Australia 3015 km (1870 miles) E of JAKARTA, Java, Indonesia |
| Location Uncertainty | horizontal +/- 4.8 km (3.0 miles); depth fixed by location program |
| Parameters | NST=265, Nph=265, Dmin=>999 km, Rmss=1.04 sec, Gp= 18°, M-type=regional moment magnitude (Mw), Version=Q |
| Source |
|
| Event ID | us2009bjca |
- This event has been reviewed by a seismologist.
- Did you feel it? Report shaking and damage at your location. You can also view a map displaying accumulated data from your report and others.
Earthquake Summary
Felt Reports
Damage and casualties are included with the event at 19:33 UTC. Felt (VII) at Manokwari, (VI) at Sorong, (IV) at Nabire and (III) at Biak.
Tectonic Summary
The magnitude 7.4 Papua, Indonesia earthquake of January 3, 2009, 22:33 UTC, occurred as a result of thrust faulting on a plate-boundary along the northwest coast of the island of New Guinea. Eastern Indonesia is characterized by complex tectonics in which motions of numerous small plates are accommodating large-scale convergence between the Australia, Pacific, and Eurasia plates. In broad-scale plate-tectonic models that do not subdivide continent sized plates into smaller plates, the location of today's earthquake would be on the boundary of the Pacific and Australia plates. The Pacific plate (located north and northeast of the epicenter) is moving southwest with respect to the Australia plate (located south of the epicenter) with a velocity of about 112 mm/year at the epicenter of the earthquake, and the focal-mechanism of today's earthquake is broadly consistent with Pacific plate lithosphere being subducted beneath Australia plate lithosphere. The subduction zone along the northwest coast of New Guinea is characterized by an offshore oceanic trench, the New Guinea trench, but teleseismically recorded earthquake hypocenters do not show a well-developed inclined seismic zone (a Wadati-Benioff zone) dipping south-southwest from the trench.
The earthquake of January 3, 2009, 22:33 UTC, occurred about 400 km west of the magnitude 8.2 earthquake of February 17, 1996. The 1996 earthquake produced a tsunami that was destructive on the island of Biak. At least 108 people were killed by the 1996 earthquake and associated tsunami.
The magnitude 7.4 earthquake of January 3, 2009, 22:33 UTC, had the same focal-mechanism as the magnitude 7.6 shock of the same date, 19:43 UTC, and was located about 70 km east of the earlier shock. It was almost certainly triggered by the earlier earthquake. Seismologists sometimes refer to a pair of similarly sized shocks that occur at nearly the same time and location as an earthquake "doublet."
Earthquake Information for Indonesia
 Tsunami Information
Tsunami Information
- NOAA West Coast & Alaska Tsunami Warning Center
- NOAA Pacific Tsunami Warning Center
- Tsunami Information Links
The earthquake locations and magnitudes cited in these NOAA tsunami bulletins are very preliminary and may be superceded by USGS locations and magnitudes computed using more extensive data sets.
Earthquake Maps
Scientific & Technical Information
- Preliminary Earthquake Report
- U.S. Geological Survey, National Earthquake Information Center:
World Data Center for Seismology, Denver

 Feeds & Data
Feeds & Data