 |
|
 |
 |
 |
Fact Sheets and At–a–Glance Reports
Cholesterol Fact Sheet
This document is also available in Portable
Document Format (PDF - 84K)
Learn more about
PDFs.
Percent of persons who had their blood cholesterol
checked within the prior five years, Adults aged 20 years and older, 2003.
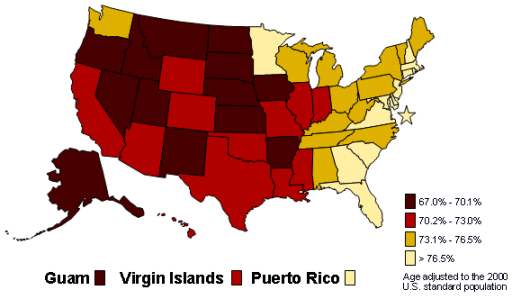
Source: CDC, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
[A text
version of this graphic is also available.]
Facts on Cholesterol
- Cholesterol is a waxy,
fat-like substance found in your body and is needed for the body to
function normally. Your body makes enough cholesterol for its needs.
When there is too much cholesterol in your body—because of diet and the rate at which
the cholesterol is processed—it is deposited in
arteries, including those of the heart, which can lead to narrowing of
the arteries and heart disease.
- An estimated 106.9 million American adults have total blood
cholesterol levels of 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and higher,
which is above desirable levels. Of these, 37.7 million have levels of
240 mg/dL or higher, which is considered high risk. (Statistics from
CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics as published by the
American Heart Association, Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics — 2005 Update.
Dallas, TX: AHA, 2004. http://www.americanheart.org*).
- Studies among people
with heart disease have shown that lowering cholesterol can reduce the
risk for dying from heart disease, having a nonfatal heart attack, and
needing heart bypass surgery or angioplasty.
- Studies among people
without heart disease have shown that lowering cholesterol can reduce
the risk for developing heart disease, including heart attacks and
deaths related to heart
disease. This is true for those with high cholesterol
levels and even for those with average levels.
- A lipoprotein profile
can be done to measure several different kinds of cholesterol as well as
triglycerides (another kind of fat found in the blood). Desirable or
optimal levels for persons with or without existing
heart disease are
Total cholesterol: Less
than 200 mg/dL.
Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol ("bad" cholesterol): Less than 100
mg/dL.
High Density
Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol ("good" cholesterol): 40 mg/dL or
higher.
Triglycerides: Less
than 150 mg/dL.
- The National
Cholesterol Education Program recommends that adults have their
cholesterol levels checked at least every 5 years.
CDC's Public Health Efforts
CDC currently funds
health departments in 32 states and the District of Columbia to develop
effective strategies to reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases and
related risk factors with an overarching emphasis on heart healthy
policies and physical and social environmental changes. Through these
state programs, CDC aims to reduce disparities in treatment, risk
factors, and disease; delay the onset of disease; postpone death from
cardiovascular disease; and reduce disabling conditions. For more
information on CDC's Cardiovascular Health State Program, please visit our
Web site at http://www.cdc.gov/cvh/state_program/index.htm
For More Information
For more information
about cholesterol, visit the Web sites:
American Heart
Association
http://www.americanheart.org/*
National Heart, Lung,
and Blood Institute
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov
Third Report of the
Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood
Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III)
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/cholesterol/index.htm
Return to Top of Page
*Links to non–Federal organizations are provided solely as a service to our users. Links do not constitute an endorsement of any organization by CDC or the Federal Government, and none should be inferred. The CDC is not responsible for the content of the individual organization Web pages found at this link.
Date last reviewed:
05/12/2006
Content source: Division for Heart Disease and Stroke
Prevention,
National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and
Health Promotion |
 |