|
PEDIATRICS Vol. 118 No. 1 July 2006, pp. 405-420 (doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1231)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
POLICY STATEMENT |
Identifying Infants and Young Children With Developmental Disorders in the Medical Home: An Algorithm for Developmental Surveillance and Screening
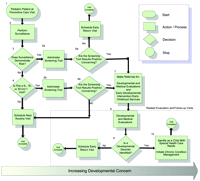
Council on Children With Disabilities, Section on Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics, Bright Futures Steering Committee and Medical Home Initiatives for Children With Special Needs Project Advisory CommitteeEarly identification of developmental disorders is critical to the well-being of children and their families. It is an integral function of the primary care medical home and an appropriate responsibility of all pediatric health care professionals. This statement provides an algorithm as a strategy to support health care professionals in developing a pattern and practice for addressing developmental concerns in children from birth through 3 years of age. The authors recommend that developmental surveillance be incorporated at every well-child preventive care visit. Any concerns raised during surveillance should be promptly addressed with standardized developmental screening tests. In addition, screening tests should be administered regularly at the 9-, 18-, and 30-month visits. (Because the 30-month visit is not yet a part of the preventive care system and is often not reimbursable by third-party payers at this time, developmental screening can be performed at 24 months of age. In addition, because the frequency of regular pediatric visits decreases after 24 months of age, a pediatrician who expects that his or her patients will have difficulty attending a 30-month visit should conduct screening during the 24-month visit.) The early identification of developmental problems should lead to further developmental and medical evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment, including early developmental intervention. Children diagnosed with developmental disorders should be identified as children with special health care needs, and chronic-condition management should be initiated. Identification of a developmental disorder and its underlying etiology may also drive a range of treatment planning, from medical treatment of the child to family planning for his or her parents.
|
Key Words: development • developmental disorders • developmental screening • disabilities • children with special health care needs • early intervention • medical home
Abbreviations: AAP—American Academy of Pediatrics • CPT—Current Procedural Terminology
The following policy statement has been revised:
- Developmental Surveillance and Screening of Infants and Young Children
- Committee on Children With Disabilities
Pediatrics 2001 108: 192-195.[Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF]
This article has been cited by other articles:
 |
M. K. Fagan and T. R. Montgomery Managing Referrals for Children with Receptive Language Delay Clinical Pediatrics, January 1, 2009; 48(1): 72 - 80. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
J. E. Roberts, J. B. Mankowski, J. Sideris, B. D. Goldman, D. D. Hatton, P. L. Mirrett, G. T. Baranek, J. S. Reznick, and D. B. Bailey Jr Trajectories and Predictors of the Development of Very Young Boys with Fragile X Syndrome J. Pediatr. Psychol., December 12, 2008; (2008) jsn129v1. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. A. Snyder, C. S. Wixson, D. Talapatra, and A. T. Roach Assessment in Early Childhood: Instruction-Focused Strategies to Support Response-to-Intervention Frameworks Assessment for Effective Intervention, December 1, 2008; 34(1): 25 - 34. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
C. E. Long, M. J. Gurka, and J. A. Blackman Family Stress and Children's Language and Behavior Problems: Results From the National Survey of Children's Health Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, November 1, 2008; 28(3): 148 - 157. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
L. Sices, D. Drotar, A. Keilman, H. L. Kirchner, D. Roberts, and T. Stancin Communication About Child Development During Well-Child Visits: Impact of Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status Screener With or Without an Informational Video Pediatrics, November 1, 2008; 122(5): e1091 - e1099. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
K. Marks, F. P. Glascoe, G. P. Aylward, M. I. Shevell, P. H. Lipkin, and J. K. Squires The Thorny Nature of Predictive Validity Studies on Screening Tests for Developmental-Behavioral Problems Pediatrics, October 1, 2008; 122(4): 866 - 868. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
D. Drotar, T. Stancin, P. H. Dworkin, L. Sices, and S. Wood Selecting Developmental Surveillance and Screening Tools Pediatr. Rev., October 1, 2008; 29(10): e52 - e58. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
D. L. Robins Screening for autism spectrum disorders in primary care settings Autism, September 1, 2008; 12(5): 537 - 556. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
S. M. Horwitz, K. E. Hoagwood, A. Garner, M. Macknin, T. Phelps, S. Wexberg, C. Foley, J. C. Lock, J. E. Hazen, R. Sturner, et al. No Technological Innovation Is a Panacea: A Case Series in Quality Improvement for Primary Care Mental Health Services Clinical Pediatrics, September 1, 2008; 47(7): 685 - 692. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
M. Sadof Discussing Illness at Well-Child Care Visits Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, August 1, 2008; 162(8): 794 - 795. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
C. M. Lannon, K. Flower, P. Duncan, K. S. Moore, J. Stuart, and J. Bassewitz The Bright Futures Training Intervention Project: Implementing Systems to Support Preventive and Developmental Services in Practice Pediatrics, July 1, 2008; 122(1): e163 - e171. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
L. W. Desch, D. Gaebler-Spira, and and the Council on Children With Disabilities Prescribing Assistive-Technology Systems: Focus on Children With Impaired Communication Pediatrics, June 1, 2008; 121(6): 1271 - 1280. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
M. J. Briggs-Gowan and A. S. Carter Social-Emotional Screening Status in Early Childhood Predicts Elementary School Outcomes Pediatrics, May 1, 2008; 121(5): 957 - 962. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
K. B. Brothers, F. P. Glascoe, and N. S. Robertshaw PEDS: Developmental Milestones--An Accurate Brief Tool for Surveillance and Screening Clinical Pediatrics, April 1, 2008; 47(3): 271 - 279. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. C. High and and the Committee on Early Childhood, Adoption, an School Readiness Pediatrics, April 1, 2008; 121(4): e1008 - e1015. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
D. S. Ross, W. J. Holstrum, M. Gaffney, D. Green, R. F. Oyler, and J. S. Gravel Hearing Screening and Diagnostic Evaluation of Children With Unilateral and Mild Bilateral Hearing Loss Trends in Amplification, March 1, 2008; 12(1): 27 - 34. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
C. P. Johnson Recognition of Autism Before Age 2 Years Pediatr. Rev., March 1, 2008; 29(3): 86 - 96. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
I. O. Ertem, D. G. Dogan, C. G. Gok, S. U. Kizilates, A. Caliskan, G. Atay, N. Vatandas, T. Karaaslan, S. G. Baskan, and D. V. Cicchetti A Guide for Monitoring Child Development in Low- and Middle-Income Countries Pediatrics, March 1, 2008; 121(3): e581 - e589. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
R. Rose-Jacobs, M. M. Black, P. H. Casey, J. T. Cook, D. B. Cutts, M. Chilton, T. Heeren, S. M. Levenson, A. F. Meyers, and D. A. Frank Household Food Insecurity: Associations With At-Risk Infant and Toddler Development Pediatrics, January 1, 2008; 121(1): 65 - 72. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
Newborn Screening Authoring Committee Newborn Screening Expands: Recommendations for Pediatricians and Medical Homes Implications for the System Pediatrics, January 1, 2008; 121(1): 192 - 217. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
F. P. Glascoe, M. M. Macias, L. M. Wegner, and N. S. Robertshaw Can a Broadband Developmental-Behavioral Screening Test Identify Children Likely to Have Autism Spectrum Disorder? Clinical Pediatrics, December 1, 2007; 46(9): 801 - 805. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
Council on Children With Disabilities Role of the Medical Home in Family-Centered Early Intervention Services Pediatrics, November 1, 2007; 120(5): 1153 - 1158. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
C. P. Johnson, S. M. Myers, and and the Council on Children With Disabilities Identification and Evaluation of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorders Pediatrics, November 1, 2007; 120(5): 1183 - 1215. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
Joint Committee on Infant Hearing Year 2007 Position Statement: Principles and Guidelines for Early Hearing Detection and Intervention Programs Pediatrics, October 1, 2007; 120(4): 898 - 921. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. H. Lipkin 17 practices help identify processes to improve developmental screening AAP News, September 1, 2007; 28(9): 12 - 12. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
A. J. Newmeyer, S. Grether, C. Grasha, J. White, R. Akers, C. Aylward, K. Ishikawa, and T. deGrauw Fine Motor Function and Oral-Motor Imitation Skills in Preschool-Age Children With Speech-Sound Disorders Clinical Pediatrics, September 1, 2007; 46(7): 604 - 611. [Abstract] [PDF] |
||||
 |
H. Hix-Small, K. Marks, J. Squires, and R. Nickel Impact of Implementing Developmental Screening at 12 and 24 Months in a Pediatric Practice Pediatrics, August 1, 2007; 120(2): 381 - 389. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
K. Marks Should General Pediatricians Not Select the Ages & Stages Questionnaire in Light of the Rydz et al Study? Pediatrics, August 1, 2007; 120(2): 457 - 458. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. H. Lipkin Should General Pediatricians Not Select the Ages & Stages Questionnaire in Light of the Rydz et al Study?: In Reply Pediatrics, August 1, 2007; 120(2): 459 - 459. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
M. D. Sadof and B. L. Nazarian Caring for Children Who Have Special Health-care Needs: A Practical Guide for the Primary Care Practitioner Pediatr. Rev., July 1, 2007; 28(7): e36 - e42. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. J. Pivalizza Early Autism Identification Pediatrics, June 1, 2007; 119(6): 1253 - 1253. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
V. B. Gupta, On behalf of the AAP Autism Expert Panel, P. H. Lipkin, and On behalf of the AAP Policy Revision Committee on Early Autism Identification: In Reply Pediatrics, June 1, 2007; 119(6): 1253 - 1254. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
E. B. Caronna, M. Augustyn, and B. Zuckerman Revisiting Parental Concerns in the Age of Autism Spectrum Disorders: The Need to Help Parents in the Face of Uncertainty Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, April 1, 2007; 161(4): 406 - 408. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
F. P. Glascoe and J. Squires Issues With the New Developmental Screening and Surveillance Policy Statement Pediatrics, April 1, 2007; 119(4): 861 - 862. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. H. Lipkin Issues With the New Developmental Screening and Surveillance Policy Statement: In Reply Pediatrics, April 1, 2007; 119(4): 862 - 863. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. H. Lipkin and H. Gwynn Improving Developmental Screening: Combining Parent and Pediatrician Opinions With Standardized Questionnaires Pediatrics, March 1, 2007; 119(3): 655a - 656. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
V. B. Gupta, S. L. Hyman, C. P. Johnson, J. Bryant, B. Byers, R. Kallen, S. E. Levy, S. M. Myers, A. I. Rosenblatt, and M. Yeargin-Allsopp Identifying Children With Autism Early? Pediatrics, January 1, 2007; 119(1): 152 - 153. [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
Developmental Surveillance and Screening in Primary Care: A New AAP Policy Statement Journal Watch Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, November 1, 2006; 2006(1101): 1 - 1. [Full Text] |
||||
 |
W. J. Barbaresi, S. K. Katusic, and R. G. Voigt Autism: A Review of the State of the Science for Pediatric Primary Health Care Clinicians. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med, November 1, 2006; 160(11): 1167 - 1175. [Abstract] [Full Text] [PDF] |
||||
 |
P. H. Lipkin 17 practices implement AAP policy on developmental screening AAP News, September 1, 2006; 27(9): 17 - 17. [Full Text] |
||||