USGS Contributions to the Climate Change Science Program
IMPACTS OF VOLCANIC EMISSIONS
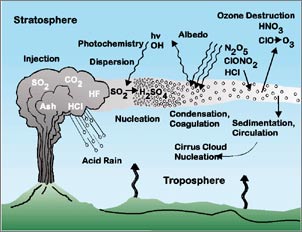
Gases from volcanoes give rise to numerous impacts on climate, the environment, and people. U.S. Geological Survey scientists are inventorying gas emissions at many of the almost 70 active volcanoes in the United States. This effort helps build a better understanding of the dynamic processes at work on the Earth's surface and is contributing important new information on how volcanic emissions affect global change. A significant component of volcanic gas research involves measuring the quantities of gas that volcanoes release into the atmosphere. Huge amounts of volcanic gas, aerosol droplets, and ash are injected into the stratosphere during major explosive eruptions. Some gases, such as carbon dioxide, are greenhouse gases that promote global warming, while others, like sulfur dioxide, can cause global cooling, ozone destruction, and polluted air known as volcanic smog or "vog". Studies of volcanic emissions allow scientists to compare volcanic gas output to emissions from man-made sources and to assess the effects of both past and future eruptions on the Earth's climate.
| USGS researchers collecting samples from the Pu'u O'o vent of the Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, to determine the kinds and amounts of gases and particles emitted. |

|
U.S. Department of the Interior | U.S. Geological Survey
URL: http://geochange.er.usgs.gov/poster/volcanicemissions.html
Page Contact Information: ESD Web Team
Page Last Modified: Thu 15-May-2003 13:22:46 MDT
Accessibility, Privacy, and other policies and notices