September Is National Gynecologic Cancer Awareness Month
 All women are at risk for cancers affecting the reproductive organs, including cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal and vulvar cancers.
All women are at risk for cancers affecting the reproductive organs, including cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal and vulvar cancers.
In 20041 more than 73,000 women in the United States were diagnosed with a cancer affecting the reproductive organs, and more than 27,000 women died from some form of gynecologic cancer.2
All women are at risk for gynecologic cancers.
Five main types of cancer affect a woman's reproductive organs: cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar. As a group, they are referred to as gynecologic (GY-neh-kuh-LAH-jik) cancer. (A sixth type of gynecologic cancer is the very rare fallopian tube cancer.)
Cervical Cancer
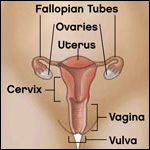
When cancer starts in the cervix, or lower end of the uterus, it is called cervical cancer. Cervical cancer is the easiest female cancer to prevent because a screening test called the Pap test and a vaccine are available. It is also highly curable when found and treated early.
Getting a Pap test regularly can find precancerous cell changes that can be treated so that cervical cancer is prevented.
If you are 11–26 years old, you can help prevent cervical cancer by getting the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine. It protects against the types of HPV that most often cause cervical, vaginal, and vulvar cancers, and is given in a series of three shots. The vaccine is recommended for girls who are 11 to 12 years old, but can be given to girls who are 9 to 10 years old. It also can be given to females who are 13–26 years old who did not get any or all of the shots when they were younger. Learn more at HPV Vaccination.
All women are at risk for cervical cancer. It occurs most often in women aged 30 years or older.2
Ovarian Cancer
When cancer starts in the ovaries, it is called ovarian cancer. Women have two ovaries that are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries make female hormones and produce eggs. When ovarian cancer is found in its early stages, treatment is most effective.
All women are at risk for ovarian cancer, but older women are more likely to get the disease than younger women.
Ovarian cancer causes more deaths than any other gynecologic cancer, but it accounts for only about 3 percent of all cancers in women.2
Uterine Cancer

When cancer starts in the uterus, it is called uterine cancer. The uterus is the pear-shaped organ in a woman's pelvis (the area below the stomach and between the hip bones).
The most common type of uterine cancer is also called endometrial cancer because it forms in the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. When uterine cancer is found and treated early, treatment is most effective.
All women are at risk for uterine cancer, but the risk increases with age. Most uterine cancers are found in women who are going through, or who have gone through, menopause—the time of life when menstrual periods stop.
Vaginal and Vulvar Cancers
When cancer starts in the vagina, it is called vaginal cancer. The vagina, also called the birth canal, is the hollow, tube-like channel between the bottom of the uterus and the outside of the body. When cancer starts in the vulva, it is called vulvar cancer. The vulva is the outer part of the female genital organs.
Vaginal and vulvar cancers are very rare. While all women are at risk for these cancers, very few will get them.
More Information
- Gynecologic Cancer Awareness
- Gynecologic Cancer Fact Sheets
- Cervical Cancer (
 283KB)
283KB) - Ovarian Cancer (
 329KB)
329KB) - Uterine Cancer (
 334KB)
334KB) - Vaginal and Vulvar Cancers (
 319KB)
319KB)
- Cervical Cancer (
- Podcasts
- Women: Be Aware (
 3:37 minutes)
3:37 minutes) - Take Time to Save Your Life (
 3:27 minutes)
3:27 minutes) - Pap Tests and Foreign-born Women, 2007 (
 6:38 minutes)
6:38 minutes)
- Women: Be Aware (
- Cáncer de cuello uterino (Spanish)
- Cáncer de ovario (Spanish)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- National Cancer Institute
1The most recent year for which statistics are currently available.
2U.S. Cancer Statistics Working Group. United States Cancer Statistics: 2004 Incidence and Mortality. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute; 2007.


