NSF's public investment in science, engineering, education and technology
helps to create knowledge and sustain prosperity. Read here about the Internet,
microbursts, Web browsers, extrasolar planets, and more... a panoply of discoveries
and innovations that began with NSF support.
 |
 |
Cheaper Plastic Solar Cells in the Works
South Dakota State University’s Diane Hinkens describes her work in an interdisciplinary research collaboration that is trying to design, synthesize and eventually fabricate a more efficient and less costly solar cell
Released
January 13, 2009
|
 |
 |
 |
Lab Tests Show Wind Turbine's Air Flow
Researcher describes NSF-supported wind tunnel experiments that mimic atmospheric airflow around wind turbines to advance our understanding of real wind farm conditions
Released
November 25, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Nanoparticles Taught to Swim
NSF-supported research team at Penn State creates nanoscale motors powered by catalytic reactions that convert chemical energy into motion
Released
November 20, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Gut Reaction: Digestion Revealed in 3-D
James Brasseur and his multidisciplinary team image the dynamic mixing of fluids and nutrient exchange in the human digestive system
Released
October 17, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
How to Make Adhesive as Good as a Gecko
Materials scientist Ali Dhinojwala and his team use nanotechnology to develop adhesive tapes that stick better than a gecko’s foot
Released
October 16, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Students Give High Marks to First U.S.-Japan Glass Science School
Meeting brings U.S. university students and researchers together with their Japanese counterparts to talk about new developments and potential collaborations in glass research
Released
August 21, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Teaching Computers How to Write Fast Software
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University develop a framework to replace the human programmer in high performance numerical library development
Released
August 8, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Natural Bio-Army Trained to Fight Cancer
Bioengineer Tarek Fahmy and colleagues are engineering new nanoscopic and microscopic biomaterials to stimulate the body’s production of killer T-cells to fight infectious diseases
Released
August 8, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Supercapacitors Could Be Key to a Green Energy Future
John Chmiola, a doctoral student at Drexel University, is doing groundbreaking work on supercapacitors
Released
July 30, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Stem Cell Research Goes Beyond Biology
Todd McDevitt tells how engineering can help us understand stem cell differentiation and develop approaches to realize the potential of stem cells for regenerative therapies
Released
July 17, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
Scientist Explores Invisible Environmental Helpers
Researcher uses his expertise in catalysis to impact major environmental issues
Released
April 25, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
2007: Year in Review
A look back at some of the NSF-supported advances and activities reported last year
Released
January 30, 2008
|
 |
 |
 |
The Science of All Things Squishy
NSF-funded Emory researcher shares the excitement of cutting-edge physics phenomena with kids of all ages
Released
August 16, 2007
|
 |
 |
 |
Life Can Be a Strain
From enormous mining trucks to human knee implants, sensor technology is teaching us when enough is enough
Released
February 21, 2007
|
 |
 |
 |
2006: Year in Review
A look back at some of the NSF-supported activities highlighted last year
Released
January 9, 2007
|
 |
 |
 |
Nanotubes Not for Toothpaste . . . Yet
Researchers Squeeze Even Rock-Hard Materials Through Minuscule Carbon Tubes
Released
July 25, 2006
|
 |
 |
 |
Purple Haze
Ancient pigment reveals secrets about unusual state of matter
Released
July 11, 2006
|
 |
 |
 |
Micro Pills Could Deliver Drugs on Demand
Temperature-sensitive capsules release chemicals at tightly controlled rates
Released
March 27, 2006
|
 |
 |
 |
From Fingerprints to Fiberprints
Forensic technique leads to new method for creating nanofibers
Released
February 15, 2006
|
 |
 |
 |
Istanbul Overdue for Earthquake Retrofit
Researchers present concerns to Turkish Prime Minister
Released
January 5, 2006
|
 |
 |
 |
Computer Program Streamlines Complex Work Scheduling
Chemical engineers develop an algorithm that could transform scheduling
Released
December 6, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
New Sensor Based on Human Organ Is No Tin Ear
Precision micromachining yields life-size, precise, artificial cochlea
Released
November 3, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
Earthquake Study Suggests Simple Building Fixes Can Save Lives
Code enforcement may have prevented dozens of deaths in Turkish temblor
Released
October 13, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
The World’s Smallest Fountain Pen?
New microscope tips use capillary action to print patterns tens of nanometers across
Released
October 5, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
Modified Collagen Could Be a Boon for Medicine
Altered protein could help shape the growth of engineered tissue
Released
September 20, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
Waves of Power
New buoys convert the ocean's energy into electricity
Released
May 17, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
Creative Minds Mingle: Robotics at the Junction of Art and Engineering
What happens when the real world meets the virtual one? Or, when the art world meets the world of engineering? A New York art professor and her students find out, through the eyes of a roaming robot named Kiru.
Released
May 6, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
Robots in the OR -- Stat!
Penelope the robot may free nurses to do more "human" tasks
Released
April 28, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
Nano-engineered Powders Tackle Toxic Chemicals
Thirsty grains act fast to clean up messes
Released
April 28, 2005
|
 |
 |
 |
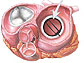
Artificial Heart Valves Face the Curdled Milk Test
A graduate student and her colleagues have developed what they think is a better way to test artificial heart valves. Using curdled milk as a blood substitute, their approach could improve preclinical testing of new devices, saving money and lives.
Released
April 26, 2005
|
 |
Page: Previous |