|
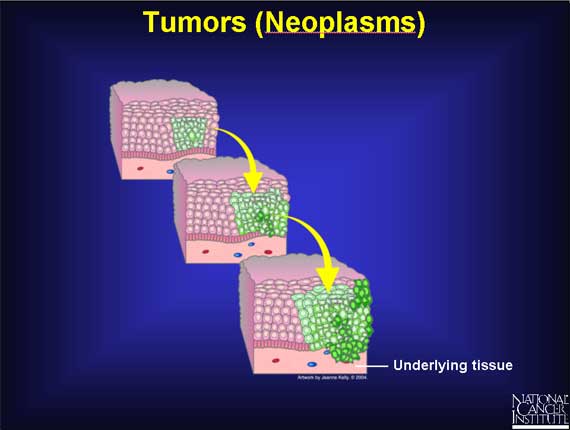
This gradual increase in the number of dividing cells creates a growing mass of tissue called a "tumor" or "neoplasm." If the rate of cell division is relatively rapid, and no "suicide" signals are in place to trigger cell death, the tumor will grow quickly in size; if the cells divide more slowly, tumor growth will be slower. But regardless of the growth rate, tumors ultimately increase in size because new cells are being produced in greater numbers than needed. As more and more of these dividing cells accumulate, the normal organization of the tissue gradually becomes disrupted.
< Previous | Index | Next Slide > |