|
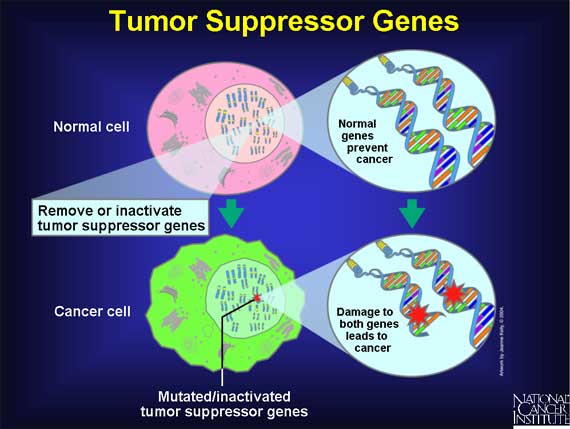
A second group of genes implicated in cancer are the "tumor suppressor genes." Tumor suppressor genes are normal genes whose ABSENCE can lead to cancer. In other words, if a pair of tumor suppressor genes are either lost from a cell or inactivated by mutation, their functional absence might allow cancer to develop. Individuals who inherit an increased risk of developing cancer often are born with one defective copy of a tumor suppressor gene. Because genes come in pairs (one inherited from each parent), an inherited defect in one copy will not lead to cancer because the other normal copy is still functional. But if the second copy undergoes mutation, the person then may develop cancer because there no longer is any functional copy of the gene.
< Previous | Index | Next Slide > |