|
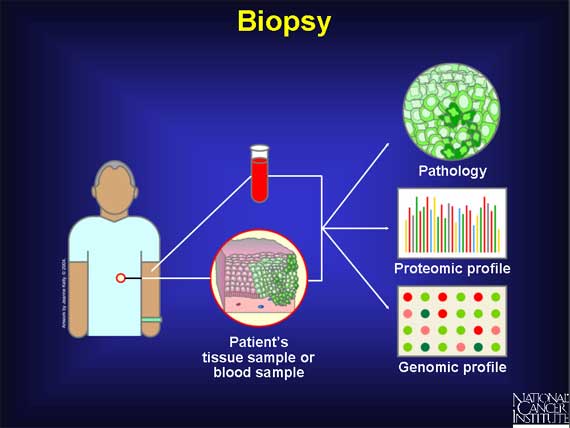
To diagnose the presence of cancer, a doctor must look at a sample of the affected tissue under the microscope. Hence, when preliminary symptoms, Pap test, mammogram, PSA test, FOBT, or colonoscopy indicate the possible existence of cancer, a doctor must then perform a biopsy, which is the surgical removal of a small piece of tissue for microscopic examination. (For leukemias, a small blood sample serves the same purpose.) This microscopic examination will tell the doctor whether a tumor is actually present and, if so, whether it is malignant (i.e., cancer) or benign. In addition, microarrays may be used to determine which genes are turned on or off in the sample, or proteomic profiles may be collected for an analysis of protein activity. This information will help doctors to make a more accurate diagnosis and may even help to inform treatment planning.
< Previous | Index | Next Slide > |