Literacy
Literacy is an important skill that enables people to communicate and function in
society.45 Everyday tasks such as reading a newspaper, balancing a checkbook, or
applying for a job require an adequate level of literacy.
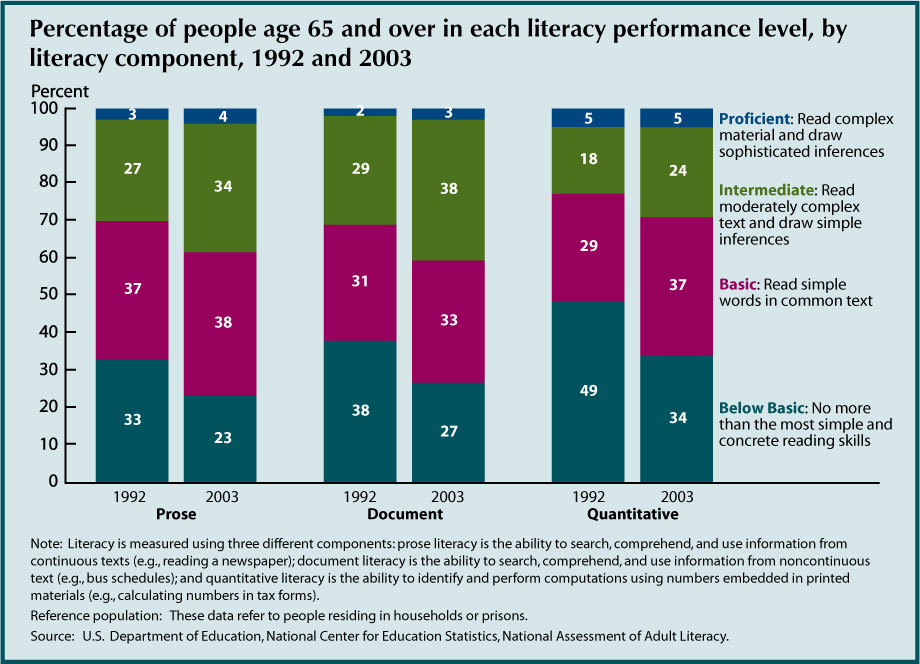
- The majority of older Americans face literacy challenges.
In 2003, 60 percent of people age 65 and over had below basic or basic document
and prose literacy, and 71 percent had below basic or basic quantitative literacy.
Only 3 percent to 5 percent of older Americans had proficient literacy in any component.
- Between 1992 and 2003, the percentage of older Americans
that had below basic prose, document, and quantitative literacy decreased significantly,
from 33 percent to 23 percent for prose, from 38 percent to 27 percent for document,
and from 49 percent to 34 percent for quantitative.
Health Literacy
Health literacy is the degree to which people have the capacity to obtain, process,
and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate
health decisions.46-48 Adhering to prescription instructions, filling out a patient
information form, or giving informed consent are specific tasks that require more
than just an adequate level of literacy—they require an adequate level of
health literacy.
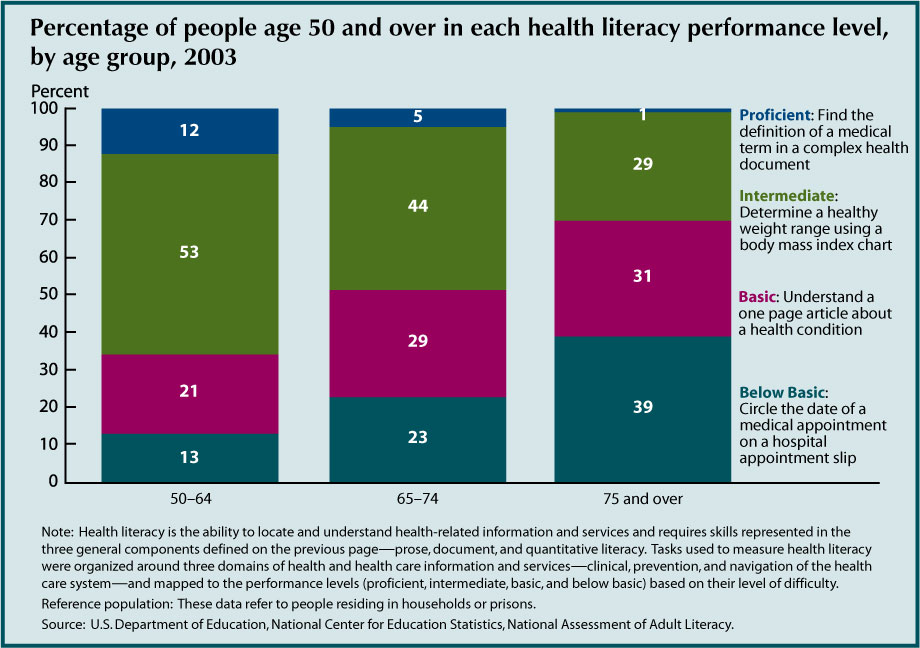
- Older adults are proportionately more likely to have
below basic health literacy than any other age group. Almost two-fifths (39 percent)
of people age 75 and over have a health literacy level of below basic compared with
23 percent of people age 65–74 and 13 percent of people age 50–64.
- Current levels of health literacy among people age
50-64 suggest fewer people 65 and over will have below basic levels of health literacy.
This is important because poor health literacy is associated with cognitive decline
among those age 80 and over, a group that is increasing in size.49