Diabetes Dictionary: P - T
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
The Diabetes Dictionary
P
pancreas (PAN-kree-us):
an organ that makes insulin and enzymes for digestion. The pancreas is located behind the lower part of the stomach and is about the size of a hand.
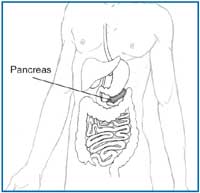
Pancreas
pancreas transplantation:
a surgical procedure to take a healthy whole or partial pancreas from a donor and place it into a person with diabetes.
pediatric (pee-dee-AT-rik) endocrinologist (en-doh-krih-NAH-luh-jist):
a doctor who treats children who have endocrine gland problems such as diabetes.
pedorthist (ped-OR-thist):
a health care professional who specializes in fitting shoes for people with disabilities or deformities. A pedorthist can custom-make shoes or orthotics (special inserts for shoes).
periodontal (PER-ee-oh-DON-tul) disease:
disease of the gums.
periodontist (PER-ee-oh-DON-tist):
a dentist who specializes in treating people who have gum diseases.
peripheral (puh-RIF-uh-rul) neuropathy (ne-ROP-uh-thee):
nerve damage that affects the feet, legs, or hands. Peripheral neuropathy causes pain, numbness, or a tingling feeling.
peripheral (puh-RIF-uh-rul) vascular (VAS-kyoo-ler) disease (PVD):
a disease of the large blood vessels of the arms, legs, and feet. PVD may occur when major blood vessels in these areas are blocked and do not receive enough blood. The signs of PVD are aching pains and slow-healing foot sores.
peritoneal dialysis:
see dialysis.
pharmacist (FAR-mah-sist):
a health care professional who prepares and distributes medicine to people. Pharmacists also give information on medicines.
Pharmacist
photocoagulation (FOH-toh-koh-ag-yoo-LAY-shun):
a treatment for diabetic retinopathy. A strong beam of light (laser) is used to seal off bleeding blood vessels in the eye and to burn away extra blood vessels that should not have grown there.
pioglitazone (py-oh-GLIT-uh-zone):
an oral medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. It helps insulin take glucose from the blood into the cells for energy by making cells more sensitive to insulin. Belongs to the class of medicines called thiazolidinediones. (Brand name: Actos.)
podiatrist (puh-DY-uh-trist):
a doctor who treats people who have foot problems. Podiatrists also help people keep their feet healthy by providing regular foot examinations and treatment.
podiatry (puh-DY-uh-tree):
the care and treatment of feet.
point system:
a meal planning system that uses points to rate the caloric content of foods.
polydipsia (pah-lee-DIP-see-uh):
excessive thirst; may be a sign of diabetes.
polyphagia (pah-lee-FAY-jee-ah):
excessive hunger; may be a sign of diabetes.
polyuria (pah-lee-YOOR-ee-ah):
excessive urination; may be a sign of diabetes.
postprandial (post-PRAN-dee-ul) blood glucose:
the blood glucose level taken 1 to 2 hours after eating.
Prandin:
see repaglinide.
Precose:
see acarbose.
pre-diabetes:
a condition in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal but are not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. People with pre-diabetes are at increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes and for heart disease and stroke. Other names for pre-diabetes are impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose.
premixed insulin:
a commercially produced combination of two different types of insulin. See 50/50 insulin and 70/30 insulin.
preprandial (pree-PRAN-dee-ul) blood glucose:
the blood glucose level taken before eating.
prevalence:
the number of people in a given group or population who are reported to have a disease.
proinsulin (proh-IN-suh-lin):
the substance made first in the pancreas and then broken into several pieces to become insulin.
proliferative (pro-LIH-fur-ah-tiv) retinopathy (REH-tih-NOP-uh-thee):
a condition in which fragile new blood vessels grow along the retina and in the vitreous humor of the eye.
prosthesis (prahs-THEE-sis):
a man-made substitute for a missing body part such as an arm or a leg.
protein (PRO-teen):
1. One of the three main nutrients in food. Foods that provide protein include meat, poultry, fish, cheese, milk, dairy products, eggs, and dried beans. 2. Proteins are also used in the body for cell structure, hormones such as insulin, and other functions.

Sources of protein
proteinuria (PRO-tee-NOOR-ee-uh):
the presence of protein in the urine, indicating that the kidneys are not working properly.
pump:
see insulin pump.
[Top]
R
rapid-acting insulin:
a type of insulin that starts to lower blood glucose within 5 to 10 minutes after injection and has its strongest effect 30 minutes to 3 hours after injection, depending on the type used. See aspart insulin and lispro insulin.
rebound hyperglycemia (HY-per-gly-SEE-mee-ah):
a swing to a high level of glucose in the blood after a low level. See Somogyi effect.
receptors:
see insulin receptors.
Recognized Diabetes Education Programs:
diabetes self-management education programs that are approved by the American Diabetes Association.
regular insulin:
short-acting insulin. On average, regular insulin starts to lower blood glucose within 30 minutes after injection. It has its strongest effect 2 to 5 hours after injection but keeps working 5 to 8 hours after injection. Also called R insulin.
renal (REE-nal):
having to do with the kidneys. A renal disease is a disease of the kidneys. Renal failure means the kidneys have stopped working.
renal threshold (THRESH-hold) of glucose:
the blood glucose concentration at which the kidneys start to excrete glucose into the urine.
repaglinide (reh-PAG-lih-nide):
an oral medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. It lowers blood glucose by helping the pancreas make more insulin right after meals. Belongs to the class of medicines called meglitinides. (Brand name: Prandin.)
retina (REH-ti-nuh):
the light-sensitive layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye.
retinopathy:
see background retinopathy, proliferative retinopathy, and diabetic retinopathy.
risk factor:
anything that raises the chances of a person developing a disease.
rosiglitazone (rose-ee-GLIH-tuh-zone):
an oral medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. It helps insulin take glucose from the blood into the cells for energy by making cells more sensitive to insulin. Belongs to the class of medicines called thiazolidinediones. (Brand name: Avandia.)
[Top]
S
saccharin (SAK-ah-rin):
a sweetener with no calories and no nutritional value.
secondary diabetes:
a type of diabetes caused by another disease or certain drugs or chemicals.
self-management:
in diabetes, the ongoing process of managing diabetes. Includes meal planning, planned physical activity, blood glucose monitoring, taking diabetes medicines, handling episodes of illness and of low and high blood glucose, managing diabetes when traveling, and more. The person with diabetes designs his or her own self-management treatment plan in consultation with a variety of health care professionals such as doctors, nurses, dietitians, pharmacists, and others.
70/30 insulin:
premixed insulin that is 70 percent intermediate-acting (NPH) insulin and 30 percent short-acting (regular) insulin.
sharps container:
a container for disposal of used needles and syringes; often made of hard plastic so that needles cannot poke through.
short-acting insulin:
a type of insulin that starts to lower blood glucose within 30 minutes after injection and has its strongest effect 2 to 5 hours after injection. See regular insulin.
side effects:
the unintended action(s) of a drug.
sliding scale:
a set of instructions for adjusting insulin on the basis of blood glucose test results, meals, or activity levels.
Somogyi (suh-MOH-jee) effect, also called rebound hyperglycemia:
when the blood glucose level swings high following hypoglycemia. The Somogyi effect may follow an untreated hypoglycemic episode during the night and is caused by the release of stress hormones.
sorbitol (SORE-bih-tall):
1. A sugar alcohol (sweetener) with 4 calories per gram. 2. A substance produced by the body in people with diabetes that can cause damage to the eyes and nerves.
split mixed dose:
division of a prescribed daily dose of insulin into two or more injections given over the course of the day.
starch:
another name for carbohydrate, one of the three main nutrients in food.
Starlix:
see nateglinide.
stroke:
condition caused by damage to blood vessels in the brain; may cause loss of ability to speak or to move parts of the body.
subcutaneous (sub-kyoo-TAY-nee-us) injection:
putting a fluid into the tissue under the skin with a needle and syringe.
sucralose:
a sweetener made from sugar but with no calories and no nutritional value.
sucrose:
a two-part sugar made of glucose and fructose. Known as table sugar or white sugar, it is found naturally in sugar cane and in beets.
sugar:
1. A class of carbohydrates with a sweet taste; includes glucose, fructose, and sucrose. 2. A term used to refer to blood glucose.
sugar alcohols:
sweeteners that produce a smaller rise in blood glucose than other carbohydrates. Their calorie content is about 2 calories per gram. Includes erythritol, hydrogenated starch hydrolysates, isomalt, lactitol, maltitol, mannitol, sorbitol, and xylitol. Also known as polyols (PAH-lee-alls.)
sugar diabetes:
former term for diabetes mellitus.
sulfonylurea (sul-fah-nil-yoo-REE-ah):
a class of oral medicine for type 2 diabetes that lowers blood glucose by helping the pancreas make more insulin and by helping the body better use the insulin it makes. (Generic names: acetohexamide, chlorpropamide, glimepiride, glipizide, glyburide, tolazamide, tolbutamide.)
syndrome x:
see insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
syringe (suh-RINJ):
a device used to inject medications or other liquids into body tissues. The syringe for insulin has a hollow plastic tube with a plunger inside and a needle on the end.
Syringe
[Top]
T
team management:
a diabetes treatment approach in which medical care is provided by a team of health care professionals including a doctor, a dietitian, a nurse, a diabetes educator, and others. The team act as advisers to the person with diabetes.
thiazolidinedione (THIGH-uh-ZOH-lih-deen-DYE-own):
a class of oral medicine for type 2 diabetes that helps insulin take glucose from the blood into the cells for energy by making cells more sensitive to insulin. (Generic names: pioglitazone and rosiglitazone.)
tight control:
see intensive therapy.
tolazamide (tohl-AH-zah-mide):
an oral medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. It lowers blood glucose by helping the pancreas make more insulin and by helping the body better use the insulin it makes. Belongs to the class of medicines called sulfonylureas. (Brand name: Tolinase.)
tolbutamide (tohl-BYOO-tah-mide):
an oral medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. It lowers blood glucose by helping the pancreas make more insulin and by helping the body better use the insulin it makes. Belongs to the class of medicines called sulfonylureas. (Brand name: Orinase.)
Tolinase:
see tolazamide.
triglyceride (try-GLISS-er-ide):
the storage form of fat in the body. High triglyceride levels may occur when diabetes is out of control.
type 1 diabetes:
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels caused by a total lack of insulin. Occurs when the body's immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas and destroys them. The pancreas then produces little or no insulin. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in young people but can appear in adults.
type 2 diabetes:
a condition characterized by high blood glucose levels caused by either a lack of insulin or the body's inability to use insulin efficiently. Type 2 diabetes develops most often in middle-aged and older adults but can appear in young people.
type I diabetes:
former term for type 1 diabetes.
type II diabetes:
former term for type 2 diabetes.
[Top]
Diabetes Dictionary Index
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
[Top]
|




