|
How can the community develop a plan for research-based prevention?
The first step in planning a drug abuse prevention program is to assess the type of drug problem within the community and determine the level of risk factors affecting the problem. The results of this assessment can be used to raise awareness of the nature and seriousness of the community’s problem and guide selection of the best prevention programs to address the problem.
Next, assessing the community’s readiness for prevention can help determine additional steps needed to educate the community before launching the prevention effort. Then, a review of current programs is needed to determine existing resources and gaps in addressing community needs and to identify additional resources.
Finally, planning can benefit from the expertise of community organizations that provide youth services. Convening a meeting with leaders of these service organizations can set the stage for capturing ideas and resources to help implement and sustain research-based programs.

How can the community use the prevention principles in prevention planning?
The prevention principles offer guidance and support for selecting and adapting effective, research-based prevention programs to meet specific community needs. For example, Principle 3 notes how a plan should address the drug problems in a community and the steps that can be taken to address them. Principle 5 explains what content to include in a family-based program.
The principles can help guide community planners in selecting the best prevention programs for their community and in providing the best strategies for putting them into effect. That way, parents, educators, and community leaders can carefully plan how, when, and where to carry out each program.
How can the community assess the level of risk for drug abuse?
To assess the level of risk of youth engaging in drug abuse, it is important to:
- measure the nature and extent of drug abuse patterns and trends;
- collect data on risk and protective factors throughout the community; and
- identify prevention efforts already under way to address the problem.
It is also important to consult with key community leaders to understand the community culture. Researchers have developed many tools, available to community planners, to assess the extent of a community’s drug problems. They include public access questionnaires and existing community-level data (e.g., truancy records, drug arrest records, emergency room admissions data). For Web sites with information on these and other assessment resources, see Selected Resources and References.
Is the community ready for prevention?
Identifying a serious level of risk in a community does not always mean that the community is ready to take action. Based on studies of many small communities, researchers have identified nine stages of "community readiness" that can guide prevention planning.24 Once prevention planners know what stage the community is in, they can take the next steps for starting prevention programming.
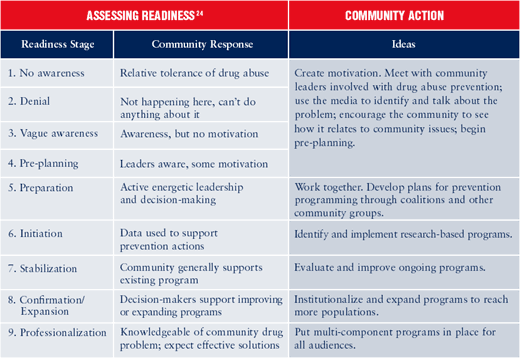
How can the community be motivated to implement research-based prevention programs?
The methods needed to motivate a community to act depend on the community’s stage of readiness so that community actions provide the maximum benefits.
One important way to effect community change is through the development of an active community anti-drug coalition. Community anti-drug coalitions can and do hold community-wide meetings, develop public education campaigns, and attract sponsors for drug abuse prevention strategies. To strengthen the impact of these strategies on community drug problems, coalitions should focus on implementing research-tested programs and approaches.
Research has shown that the media can raise public awareness about a community’s drug problem and prevent drug abuse among specific populations.
How can the community assess the effectiveness of current prevention efforts?
Many communities begin the process with a review of current prevention programs to determine:
- What programs are in place in the community?
- Were strict scientific standards used to test the programs during their development?
- Do the programs match community needs?
- Are the programs being carried out as designed?
- What percentage of at-risk youth is being reached by the programs?
Another evaluation approach is to track data over time on drug abuse among students in school, rates of truancy, school suspensions, drug abuse arrests, and drug-related emergency room admissions. Data from community drug abuse assessments can serve as a baseline for measuring change. Because drug abuse problems change with time, periodic assessments can ensure that programs are meeting current community needs.
|