|
One method of treating
patients with severe angina due to diffuse coronary disease
is transmyocardial laser revascularization (TMR).
|
2.57 MB |
|
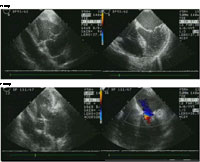
Preoperative (top panel)
echocardiography images from a patient with severe mitral
valve regurgitation. After the valve is repaired (lower panel)
the mitral valve no longer leaks. |
574 KB |
|
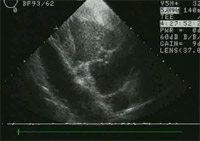
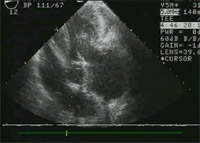
Preoperative long axis view of mitral valve with prolapsing leaflet.
|
76 KB |
|
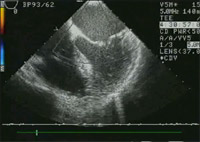
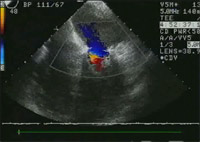
Preoperative Doppler demonstrating significant mitral regurgitation as a result of the prolapse.
|
143 KB |
|
Postoperative long axis view demonstrating coaptation of leaflets and repair of prolapse.
|
123 KB |
|
Postoperative Doppler showing resolution of mitral regurgitation.
|
119 KB |
|
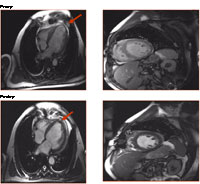
Preoperative (top panel) MR images
from a patient that had suffered a myocardial infarction and
had loss of heart muscle and function. Not only was a significant
focal area damaged and thinned (arrow), but the overall contractility
was diminished. Restoration of normal heart shape following
a surgical resection of the damage muscle (arrow) leads to
improved heart function.
|
470 KB |
|
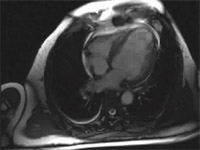
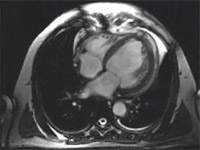
Preoperative long axis view of left ventricle with thinned infarcted apex.
|
49 KB |
|
Postoperative long axis view of left ventricle after apex removed and ventricular reconstruction.
|
71 KB |
|
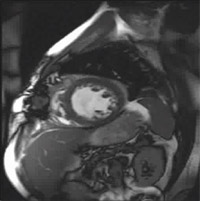
Postoperative short axis view of smaller more dynamic ventricle after reconstruction.
|
50 KB |

|
Preoperative short axis view of dilated poorly functioning ventricle.
|
72 KB |
|
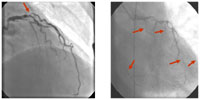
Coronary Artery
Disease: While the majority of patients with typical coronary
artery disease (fig. on left, coronary blockage denoted
by red arrow) can be treated by percutaneous interventions
or bypass surgery, there are an increasing number of patients
with diffuse coronary artery disease (fig. on right) that
are not candidates for such interventions.
|
137 KB |
|
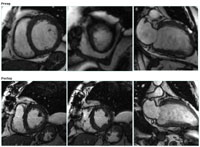
MRI : CABG + CO2
TMR: Preoperative (top row) MRI images from a patient that
underwent TMR and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
The arteries that could be bypassed were grafted and the
areas that could not be grafted due to diffuse coronary
disease were treated with TMR. Postoperatively (bottom row)
there is significant improvement in the contractility of
the heart and in addition to this improvement in function
the patient had relief from their angina.
|
14.4 KB |
|
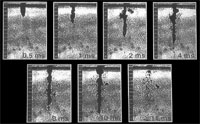
CO2 Laser-Tissue Effect: Flash
photography of the energy delivery from a CO2 laser to tissue.
|
235 KB |
|
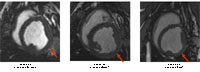
Cine MRI Images: MRI images from
animals with coronary occlusions treated with CO2 TMR that
demonstrate an improvement in function for Group 1 and 2 (arrow
identifies treated area) but a decrease in function when more
channels are created (Group 3).
|
544 KB |

|
Summary of results of TMR dose-response
curve. |
882 KB |