 Benin
Benin
Country Specific Information
On this page » |
|
April 28, 2008
COUNTRY DESCRIPTION: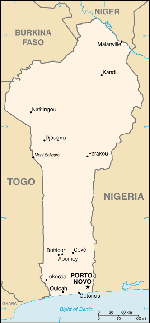
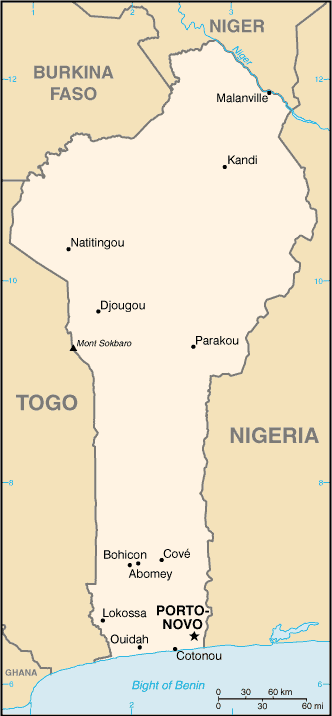 Benin is a developing country in West Africa. Its political capital is Porto Novo. However, its administrative capital,
Cotonou, is Benin's largest city and the site of most government, commercial, and tourist activity. Read the Department of
State Background Notes on Benin for additional information.
Benin is a developing country in West Africa. Its political capital is Porto Novo. However, its administrative capital,
Cotonou, is Benin's largest city and the site of most government, commercial, and tourist activity. Read the Department of
State Background Notes on Benin for additional information.
ENTRY/EXIT REQUIREMENTS: A passport and visa are required. Visas are not routinely available at the airport. Visitors to Benin should also carry the WHO Yellow Card (“Carte Jaune”) indicating that they have been vaccinated for yellow fever. Contact the Embassy of Benin for the most current visa information. The Embassy is located at: 2124 Kalorama Road NW, Washington, DC 20008; tel: 202-232-6656.
Information about dual nationality or the prevention of international child abduction can be found on our web site. For further information about customs regulations, please read our Customs Information sheet.
SAFETY AND SECURITY: U.S. citizens should avoid crowds, political rallies, and street demonstrations and maintain security awareness at all times.
U.S. citizens should not walk on the beach alone at any time of day. It is also highly recommended not to carry a passport
or valuables when walking in any part of the city. Travelers should carry a notarized photocopy of the photo page of their
passport (see Crime section). They should not walk around the city after dark, and should take particular care to avoid the
beach and isolated areas near the beach after dark.
The ocean currents along the coast are extremely strong and treacherous with rough surf and a strong undertow, and several
people drown each year.
For the latest security information, Americans traveling abroad should regularly monitor the Department of State, Bureau of Consular Affairs’ web site at http://travel.state.gov, where the current Travel Warnings and Travel Alerts, as well as the Worldwide Caution, can be found.
Up-to-date information on safety and security can also be obtained by calling 1-888-407-4747 toll free in the U.S. and Canada, or for callers outside the U.S. and Canada, a regular toll-line at 1-202-501-4444. These numbers are available from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday through Friday (except U.S. federal holidays).
The Department of State urges American citizens to take responsibility for their own personal security while traveling overseas. For general information about appropriate measures travelers can take to protect themselves in an overseas environment, see the Department of State’s pamphlet A Safe Trip Abroad.
CRIME: Street robbery is a significant problem in Cotonou. Robbery and mugging occur along the Boulevard de France (the beach road by the Marina and Novotel Hotels) and on the beaches near hotels frequented by international visitors. Most of the reported incidents involve the use of force, often by armed persons, with occasional minor injury to the victim. Travelers should avoid isolated and poorly lit areas and should not walk around the city or the beaches between dusk and dawn. Even in daylight hours, foreigners on the beach near Cotonou are frequent victims of robberies. When visiting the beach, travelers should not bring valuables and should carry only a photocopy of their passport. If you are a victim of crime, you should contact the U.S. Embassy immediately. There has been a continued increase in the number of robberies and carjacking incidents after dark, both within metropolitan Cotonou and on highways and rural roads outside of major metropolitan areas. Motorists are urged to be wary of the risk of carjacking. Keep the windows of your vehicle rolled up and the doors locked. Stay alert for signs of suspicious behavior by other motorists or pedestrians that may lead to carjacking, such as attempts to stop a moving vehicle for no obvious reason. Travelers should avoid driving outside the city of Cotonou after dark and should exercise extreme caution when driving in Cotonou after dark (see Traffic Safety and Road Conditions below). Overland travel to Nigeria is dangerous near the Benin/Nigeria border due to unofficial checkpoints and highway banditry.
Travelers should avoid the use of credit cards and automated teller machines (ATMs) in Benin due to a high rate of fraud. Perpetrators of business and other kinds of fraud often target foreigners, including Americans. While such fraud schemes in the past have been largely associated with Nigeria, they are now prevalent throughout West Africa, including Benin, and are more frequently perpetrated by Beninese criminals. Business scams are not always easy to recognize, and any unsolicited business proposal should be carefully scrutinized. There are, nevertheless, some indicators that are warnings of a probable scam. Look out for:
Any offer of a substantial percentage of a very large sum of money to be transferred into your account, in return for your "discretion" or "confidentiality";
Any deal that seems too good to be true;
Requests for signed and stamped, blank letterhead or invoices, or for bank account or credit card information;
Requests for urgent air shipment, accompanied by an instrument of payment whose genuineness cannot immediately be established;
Solicitations claiming the soliciting party has personal ties to high government officials;
Requests for payment, in advance, of transfer taxes or incorporation fees;
Statements that your name was provided to the soliciting party either by someone you do not know or by "a reliable contact";
Promises of advance payment for services to the Beninese government; and
Any offer of a charitable donation.
These scams, which may appear to be legitimate business deals requiring advance payments on contracts, pose a danger of both
financial loss and physical harm. Recently more American citizens have been targeted. The perpetrators of such scams sometimes
pose as attorneys. One common ploy is to request fees for “registration” with fictitious government offices or regulatory
authorities. The best way to avoid becoming a victim of advance-fee fraud is common sense – if it looks too good to be true,
it probably is. Travelers should carefully check out any unsolicited business proposal originating in Benin before committing
any funds, providing any goods or services, or undertaking any travel. For additional information, please see the Department
of State’s Bureau of Consular Affairs brochure, International Financial Scams.
Scams may also involve persons posing as singles on Internet dating sites or as online acquaintances who then get into trouble and require money to be "rescued." If you are asked to send money by someone you meet online please contact the U.S. Embassy before doing so.
INFORMATION FOR VICTIMS OF CRIME: The loss or theft abroad of a U.S. passport should be reported immediately to the local police and the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate. If you are the victim of a crime while overseas, in addition to reporting to local police, please contact the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate for assistance. The Embassy/Consulate staff can, for example, assist you to find appropriate medical care, contact family members or friends and explain how funds could be transferred. Although the investigation and prosecution of the crime is solely the responsibility of local authorities, consular officers can help you to understand the local criminal justice process and to find an attorney if needed.
See our information on Victims of Crime.
MEDICAL FACILITIES AND HEALTH INFORMATION: Medical facilities in Benin are limited and not all medicines are available. Travelers should bring their own supplies of prescription drugs and preventive medicines. Not all medicines and prescription drugs available in Benin are USFDA-approved. Malaria is a serious risk to travelers to Benin. For information on malaria, its prevention, protection from insect bites, and anti-malarial drugs, please visit the CDC Travelers' Health web site at http://www.cdc.gov/malaria/.
For information on avian influenza (bird flu), please refer to the Department of State's Avian Influenza Fact Sheet, available at http://travel.state.gov/travel/tips/health/health_1181.html.
Information on vaccinations and other health precautions, such as safe food and water precautions and insect bite protection, may be obtained from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s hotline for international travelers at 1-877-FYI-TRIP (1-877-394-8747) or via the CDC’s website at http://wwwn.cdc.gov/travel/default.aspx. For information about outbreaks of infectious diseases abroad consult the World Health Organization’s (WHO) web site at http://www.who.int/en. Further health information for travelers is available at http://www.who.int/ith/en.
MEDICAL INSURANCE: The Department of State strongly urges Americans to consult with their medical insurance company prior to traveling abroad to confirm whether their policy applies overseas and whether it will cover emergency expenses such as a medical evacuation. Please see our information on medical insurance overseas.
TRAFFIC SAFETY AND ROAD CONDITIONS: While in a foreign country, U.S. citizens may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Benin is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.
With the exception of the road linking Cotonou in the south to Malanville on the border with Niger in the north, and from
Parakou in central Benin to Natitingou in the northwestern part of the country, roads in Benin are generally in poor condition
and are often impassable during the rainy season. Benin's unpaved roads vary widely in quality; deep sand and potholes are
common. During the rainy season from mid-June to mid-September, dirt roads often become impassable. Four-wheel drive vehicles
with full spare tires and emergency equipment are recommended.
Most of the main streets in Cotonou are paved, but side streets are often dirt with deep potholes. Traffic moves on the right,
as in the United States. Cotonou has no public transportation system; many Beninese people rely on bicycles, mopeds, motorbikes,
and zemidjans (moped taxis). All official Americans are required to wear safety helmets when on a motorcycle and are strongly
discouraged from using zemidjans. Travelers using zemidjans, particularly at night, are much more vulnerable to being mugged,
assaulted or robbed. Buses and bush taxis offer service in the interior.
Gasoline smuggled from Nigeria is widely available in glass bottles and jugs at informal roadside stands throughout Cotonou
and much of the country. This gasoline is of unreliable quality, often containing water or other contaminants that can damage
or disable your vehicle. Drivers should purchase fuel only from official service stations. There are periodic gas shortages,
which can be particularly acute in the north of the country where there are few service stations.
U.S. citizens traveling by road should exercise extreme caution. Poorly maintained and overloaded transport and cargo vehicles
frequently break down and cause accidents. Drivers often place branches or leaves in the road to indicate a broken down vehicle
is in the roadway. Undisciplined drivers move unpredictably through traffic. Construction work is often poorly indicated. Speed
bumps, commonly used on paved roads in and near villages, are seldom indicated. Drivers must be on guard against people and
livestock wandering into or across the roads. Nighttime driving is particularly hazardous as vehicles frequently lack headlights
and/or taillights, and brake lights are often burned out.
With few exceptions, Cotonou and other cities lack any street lighting, and lighting on roads between population centers is
non-existent. The U.S. Embassy in Cotonou prohibits non-essential travel outside of metropolitan areas after dusk by official
Americans and strongly urges all U.S. citizens to avoid night driving as well. There have been numerous carjackings and robberies
on roads in Benin after dark, several of which resulted in murder when the driver refused to comply with the assailants' demands. The
National Police periodically conduct vehicle checks at provisional roadblocks in an effort to improve road safety and reduce
the increasing number of carjackings. When stopped at such a roadblock, you must have all of the vehicle's documentation available
to present to the authorities.
Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information. Visit the website of the country’s national tourist office at http://www.benintourisme.com.
AVIATION SAFETY OVERSIGHT: As there is no direct commercial air service to the United States by carriers registered in Benin, the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has not assessed Benin’s Civil Aviation Authority for compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) aviation safety standards. For more information, travelers may visit the FAA’s web site at http://www.faa.gov/safety/programs_initiatives/oversight/iasa.
SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES: U.S. citizens are advised to keep a notarized photocopy of the photo page of their passport with them at all times when
traveling in Benin.
The Embassy has had a few reports of officials requesting a "gift" to facilitate official administrative matters (e.g., customs
entry). Such requests should be politely but firmly declined.
It is prohibited to photograph government buildings and other official sites, such as military installations, without the
formal consent of the Government of Benin. In general, it is always best to be courteous and ask permission before taking
pictures of people. Beninese citizens may react angrily if photographed without their prior approval.
Obtaining customs clearance at the port of Cotonou for donated items shipped to Benin from the United States may be a lengthy
process. In addition, to obtain a waiver of customs duties on donated items, the donating organization must secure prior written
approval from the Government of Benin. Please contact the U.S. Embassy in Cotonou for more detailed information.
Please see our Customs Information.
CRIMINAL PENALTIES: While in a foreign country, a U.S. citizen is subject to that country's laws and regulations, which sometimes differ significantly from those in the United States and may not afford the protections available to the individual under U.S. law. Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Persons violating Benin laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Benin are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime, prosecutable in the United States. Please see our information on Criminal Penalties.
CHILDREN'S ISSUES: For information see our Office of Children’s Issues web pages on intercountry adoption and international parental child abduction.
REGISTRATION / EMBASSY LOCATION: Americans living or traveling in Benin are encouraged to register with the U.S. Embassy through the State Department’s travel registration web site so that they can obtain updated information on travel and security within Benin. Americans withoutInternet access may register
directly with the U.S. Embassy. By registering, American citizens make it easier for the Embassy or Consulate to contact them
in case of emergency. The U.S. Embassy is located at Rue Caporal Anani Bernard in Cotonou. The Embassy's mailing address is
B.P. 2012, Cotonou, Benin. The 24-hour telephone numbers are (229) 21-30-06-50, 21-30-05-13, and 21-30-17-92. The Embassy’s
general fax number is (229) 21-30-06-70; the Consular Section’s fax number is (229) 21-30-66-82; http://cotonou.usembassy.gov/.
* * *
This replaces the Country Specific Information for Benin dated August 17th, 2007 to update sections on Safety and Security
and Traffic Safety and Road Conditions.

