Home > Laboratory Personnel > Slide 9
Laboratory Personnel, Slide 9
Antimicrobial Susceptibillity Test E Test™ and Disk Diffusion
| Next > |
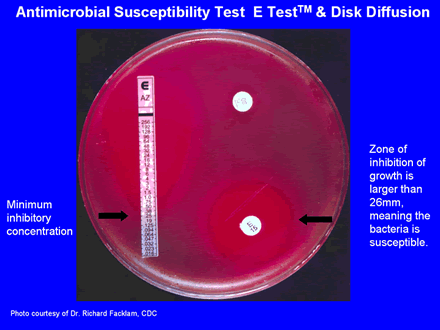
Depicted above are two methods for determining antimicrobial susceptibility of GBS. It is especially important that the microbiologist determine the susceptibility of GBS to erythromycin and clindamycin as these two drugs are used as substitutes if the patient cannot be treated with penicillin.
The long strip on the left is called the E-testTM. This pictures shows the drug azithromycin (this is shown as an example: we recommend using an erythromycin or clindamycin E-testTM). In this test, the strip contains a gradation of antibiotic with the strongest being at the top of the strip and the weakest at the bottom. The minimum inhibitory concentration of antibiotic that will inhibit the bacteria is determined by where the growth of the bacteria starts, or the area of the growth where the ellipse growth meets the strip.
The two disks on the right of the agar plate are erythromycin and tetracycline (shown here as an example: we recommend using clindamycin for GBS). There are criteria for the zones of inhibition of growth that determine whether or not the bacteria is susceptible or resistant. In the test shown above, the bacterium is susceptible to erythromycin (the zone is large >26mm) and resistant to tetracycline (zone is small <12mm). Since the disk test predictability is accurate and considerably less expensive than the e-test, in most situations, the disk test is perfectly satisfactory for determining the antimicrobial susceptibility of GBS. Users should consult the NCCLS document below for interpretation of MIC’s or zones for determining susceptible intermediate resistance or resistance.
NCCLS Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twelfth Informational Supplement: M100-12 (2002) M2-A7 and M7-A5.