Chikungunya fever is a viral disease transmitted to humans by the bite of infected mosquitoes. Chikungunya virus is a member of the genus Alphavirus, in the family Togaviridae. Chikungunya fever is diagnosed based on symptoms, physical findings (e.g., joint swelling), laboratory testing, and the possibility of exposure to infected mosquitoes. There is no specific treatment for chikungunya fever; care is based on symptoms. Chikungunya infection is not usually fatal. Steps to prevent infection with chikungunya virus include use of insect repellent, protective clothing, and staying in areas with screens. Chikungunya virus was first isolated from the blood of a febrile patient in Tanzania in 1953, and has since been cited as the cause of numerous human epidemics in many areas of Africa and Asia and most recently in limited areas of Europe.
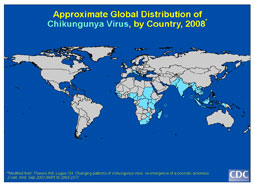
Additional information on chikungunya fever can be found using Links and References.
Content Source:
Division of Vector Borne Infectious Diseases
National Center for Zoonotic, Vector-Borne, and Enteric Diseases
