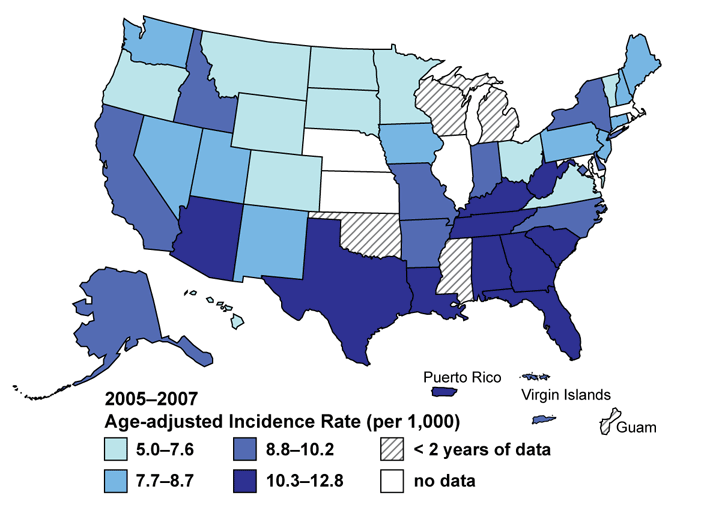
Rate of New Cases of Diabetes Among Adults, by State
To prevent diabetes, lifestyle interventions must be developed and delivered to those at risk.
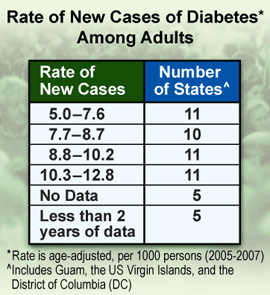
In recognition of November as American Diabetes Month, this feature highlights recently released diabetes statistics about new diabetes cases. In 2005-2007, the annual average incidence (rate of new cases) of diabetes was 9.0 new cases per 1000 persons. The highest incidence rates were found in the South and Puerto Rico.
BRFSS (Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System) is a state-based, random-digit--dialed, landline telephone survey of the U.S. civilian noninstitutionalized population aged ≥18 years and is conducted in all 50 states, DC, Guam, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Council of American Survey and Research Organizations (CASRO) participant response rates* among states ranged from 48.6% to 84.5% (median: 68.5%), and cooperation rates† ranged from 50.9% to 84.6% (median: 71.4%). In 2007, CASRO response rates among states ranged from 26.9% to 65.4% (median: 50.6%), and cooperation rates ranged from 49.6% to 84.6% (median: 72.1%). State sample sizes for 2005--2007 ranged from 7,091 in Alaska to 52,465 in Florida.
Persons with diagnosed diabetes were defined as those who answered "yes" to the question, "Have you ever been told by a doctor that you have diabetes?" Women who had been told that they had diabetes only during pregnancy and respondents told they had prediabetes or borderline diabetes were classified as not having diabetes. Those with diagnosed diabetes were then asked at what age they were diagnosed. Duration of diagnosed diabetes was calculated by subtracting the age at diagnosis from current age.
The number of incident cases of diagnosed diabetes was defined as those cases with duration of zero plus one half of the cases with duration of 1 year (1). To derive incidence rates, the number of incident cases was divided by the number of persons without diabetes plus the number of incident cases (1). Incidence was age adjusted according to the 2000 U.S. standard population and analyzed by state, territory, and U.S. Census region.§ Average annual incidence was calculated from the 3 years collected during 2005--2007; states with <2 years of data for the period were excluded. During 2005--2007, 40 participating states, DC, and two territories had ≥2 years of data; 33 participating states had ≥2 years of data for both periods. For the 33 states, incidence rates were compared using t-tests for significance. Data were weighted to respondents' probabilities of being selected and to age-, race-, and sex-specific populations from each state's annually adjusted census.
The pattern of high incidence rates in the South is consistent with previously documented high prevalence of diabetes in this region. The South also has high prevalences of modifiable risk factors for type 2 diabetes (90%--95% of all diabetes in the United States is type 2), including obesity (2) and physical inactivity (3). A recent study found the prevalence of obesity in 2007 was greatest in the South (27.3%) followed by the Midwest (26.5%), Northeast (24.4%), and West (23.1%) (2). Obesity prevalence exceeded 30% in three southern states: Alabama, Mississippi, and Tennessee. Similar regional patterns have been found for physical inactivity, for which the South had greater prevalence (17.4%), compared with the Northeast (15.7%), Midwest (14.1%), and West (11.2%) (3). Effective population-based approaches to prevent obesity and increase physical activity might help to reduce the incidence of diabetes. Efforts to prevent diabetes also should focus on persons at high risk for type 2 diabetes. In a study of persons at high risk, a 5%--10% reduction in body weight coupled with 30 minutes of moderate physical activity 5 days a week resulted in a 58% reduction in diabetes over a 3-year period (4).
* The percentage of persons who completed interviews among all eligible persons, including those who were not successfully contacted.
† The percentage of persons who completed interviews among all eligible persons who were contacted.
§ West: Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Hawaii, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Wyoming; Midwest: Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin; Northeast: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, and Vermont; and South: Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, District of Columbia, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Virginia, West Virginia, Tennessee, and Texas.
References:
- Geiss LS, Pan L, Cadwell B, Gregg EW, Benjamin SM, Engelgau MM. Changes in incidence of diabetes in U.S. adults, 1997--2003. Am J Prev Med 2006;30:371--7.
- CDC. State-specific prevalence of obesity among adults---United States, 2007. MMWR 2008;57:765—8.
- Reis JP, Bowles HR, Ainsworth BE, Dubose KD, Smith S, Laditka JN. Nonoccupational physical activity by degree of urbanization and U.S. geographic region. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2004;36:2093--8.
- Knowler WC, Barrett-Conner E, Fowler SE, et al. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention. N Engl J Med 2002;346:393--403.
Data Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. State Incidence of Diabetes Among Adults - Selected U.S. States, 1995-1997 and 2005-2007. MMWR 2008; 57(43);1169-1173.
More Information
- CDC Diabetes site
- BRFSS site
- Diabetes Data and Trends
- Listen to podcasts about diabetes
- Send a diabetes e-card


