About CDC
Hot Links
Conferences & Events
Outbreak: Plagues that changed HistorySeptember 27 – January 30, 2009
Organized by the Global Health Odyssey Museum; come see Byrn Barnard’s images of the symptoms and paths of the world’s deadliest diseases – and how the epidemics they spawned have changed history forever.
CDC Timeline
 2007
2007
CDC issues federal order of isolation, the last such order being issued in 1963.
2006
CDC celebrates 60th anniversary.
2005
Rubella was eliminated in the United States.
2004
CDC provided support for laws restricting access to over-the-counter medications used in methamphetamine production in Georgia.
2003
SARS was first reported in Asia. CDC provided guidance for surveillance, clinical and laboratory evaluation, and reporting.
 2002
2002
CDC reported that U.S. newborn HIV infections were down 80 percent since 1981.
2001
CDC learned of the first anthrax case; the victim was a 63-year-old Florida man. He would be the first in a series of domestic terrorism victims of infection by anthrax sent through the mail.
2000
Children's Health Act of 2000 established Safe Motherhood, a CDC program to better understand the burden of maternal complications and mortality.
 1999
1999
CDC’s Laboratory Response Network was established.
1998
For the first time since 1981, AIDS was diagnosed in more African-American and Hispanic men than in gay white men
1997
CDC participated in the nationally televised White House event of the Presidential Apology for the Tuskegee Study.
1996
CDC found measurable levels of serum cotinine in the blood of 88 percent of American nonsmokers.
1995
CDC recommended offering HIV testing to all pregnant women.
 1994
1994
Polio elimination certified in the Americas.
1993
CDC investigated an outbreak of a mysterious illness in the southwestern United States, later known as hantavirus.
1992
The National Academy of Sciences reported on a dangerous new phenomenon: the emergence of new and virulent diseases that are resistant to antibiotics.
1991
PHS recommended all women of childbearing years consume 400 mg of folic acid/day to reduce the risk of pregnancies affected by spina bifida and anencephaly.
 1990
1990
For the first time, CDC reported the possible transmission of HIV from a dentist to a patient in Florida during an invasive procedure.
1989
CDC reported every 6 of 10 killings involved guns, making firearms the 8th leading cause of death, after diabetes but ahead of liver disease.
1988
CDC established the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion.
1987
CDC reported that about 7,000 workers die on the job annually; 42 percent of female workers who die on the job are murdered.
1986
The Office on Smoking and Health, which targets the nation’s primary preventable health problem, became part of CDC.
1985
CDC study stated polysaccharide, a new vaccine, was a ost-effective means to protect children who were at risk for developing Haemophilus influenzae.
1984
CDC studied Vietnam veterans who were exposed to Agent Orange during combat and later fathered babies; no increased risk of birth defects was found.
1983
CDC established a Violence Epidemiology Branch to apply public health prevention strategies to child abuse, homicide, and suicide.
1982
CDC advised of the possible risk of Reye syndrome associated with the use of aspirin by children with chickenpox and flu-like symptoms.
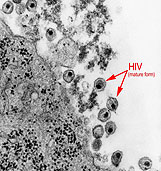 1981
1981
The first diagnosis of the fatal disease later known as AIDS was described in the June 5, 1981, issue of MMWR.
1980
MMWR published the first report on a newly recognized illness associated with tampon use: toxic shock syndrome.
1979
First Healthy People report published.
1978
Alcorn County, Mississippi, reported cases of the first outbreak of tuberculosis resistance to formerly effective drugs.
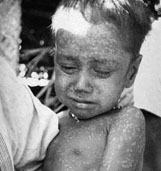 1977
1977
Global eradication of smallpox was achieved.
1976
CDC investigated two outbreaks of a previously unknown deadly hemorrhagic fever, later known as Ebola, in Zaire and Sudan.
1975
The last victim of variola major smallpox, the more severe form of the disease, was reported.
 1974
1974
CDC planned a major campaign to reverse the downward trend in the number of Americans immunized.
1973
MMWR reported that lead emissions in a residential area constituted a public health threat—contrary to popular assumption at the time.
1972
CDC assisted Sierra Leone in fighting a new outbreak of Lassa fever, a mysterious lethal viral disease
1971
The National Center for Health Statistics conducted the first National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to capture the health status of Americans.
 1970
1970
The Communicable Disease Center became the Center for Disease Control.
1969
CDC constructed a “biocontainment lab” to protect scientists while they work with deadly and infectious pathogens.
1968
CDC investigated an unidentified, highly infectious respiratory disease in Pontiac, Michigan, later identified as Legionnaire’s disease.
1967
The Foreign Quarantine Service, one of the oldest and most prestigious units of the Public Health Service, joined CDC.
 1966
1966
CDC announced a national measles eradication campaign at the American Public Health Association meeting.
1965
New surveillance systems added to the original National Surveillance Program of 1952 included measles, shigellosis, tetanus, and trichinosis.
1964
The first Surgeon General’s report linking smoking to lung cancer was released. It stated that “cigarette smoking is a health hazard of sufficient importance in the United States to warrant appropriate remedial action.”
 1963
1963
CDC tested the newly developed Jet Gun and vaccine for smallpox.
1962
CDC played a key role in one of the greatest triumphs of public health: the eradication of smallpox.
1961
CDC took over publication of Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR).
1960
The Tuberculosis Program moved from the Public Health Service to CDC.
 1959
1959
Dr. Robert Kissling developed the fluorescent antibody test for rabies, first used in a field trial with 100 percent accuracy.
1958
A CDC team traveled overseas, for the first time, to Southeast Asia to respond to an epidemic of cholera and smallpox
 1957
1957
National guidelines for influenza vaccine were developed.
1956
Dr. William Cherry found the first practical use for the fluorescent technique and used it to research communicable diseases of bacterial origin.
 1955
1955
CDC established the Polio Surveillance Program.
1954
Alexander D. Langmuir, MD, MPH, set up a leptospirosis laboratory in Jacksonville, Florida.
1953
CDC reported first case of rabies in a bat.
1952
U.S. Surgeon General Dr. Leonard A. Scheele reported that the Communicable Disease Center was ready to combat possible biological warfare.
1951
The Epidemic Intelligence Service was established to help protect against biological warfare and manmade epidemics.
 1950
1950
Fifteen CDC staffers conducted the first investigation of an epidemic of polio in Paulding County, Ohio.
1949
The US was declared free of malaria as a significant public health problem.
1948
CDC gained worldwide recognition for the quality and quantity of its contributions to the taxonomy of the Enterobacteriaceae.
1947
In San Francisco, CDC took over the Public Health Service Plague Laboratory, thus acquiring an Epidemiology Division.
1946
The Communicable Disease Center was organized in Atlanta, Georgia,
on July 1.
to the top
Page last updated: July 17, 2008
Content source: Office of Enterprise Communication
Notice: Links to non-governmental sites do not necessarily represent the views of the CDC.

