Global HIV/AIDS at CDC

![]() Extensive scientific and technical expertise
Extensive scientific and technical expertise
![]() Decades of experience addressing epidemics
Decades of experience addressing epidemics
![]() Building local capacity
Building local capacity
![]() Developing Global HIV/AIDS Resources
Developing Global HIV/AIDS Resources
![]() Global Presence
Global Presence
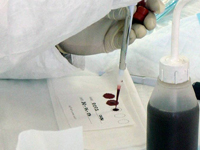 CDC created the Global AIDS Program (CDC GAP) in 2000 to address the HIV/AIDS
epidemic by assisting resource-constrained countries to:
CDC created the Global AIDS Program (CDC GAP) in 2000 to address the HIV/AIDS
epidemic by assisting resource-constrained countries to:
- Prevent HIV infection
- Improve treatment, care and support for people living with HIV
- Build vital capacity and infrastructure to address the global HIV/AIDS epidemic
CDC GAP's highly trained physicians, epidemiologists, public health advisors, behavioral scientists, and laboratory scientists support the national HIV/AIDS strategies of more than 60 countries in Africa, Asia, Central and South America, and the Caribbean through its country and regional offices.
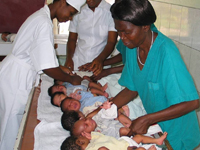 CDC plays a vital role in preventing and controlling epidemics in the United
States and across the globe. In 2003, when the President's Emergency Plan for
AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) was announced, CDC GAP joined the unified US Government
response to global HIV/AIDS. Because of its presence on the ground, CDC GAP also
is uniquely positioned to coordinate with and draw upon the strengths of CDC's
other global health programs, such as global disease detection, public health
training, and prevention and control of other infectious diseases such as
malaria and tuberculosis (TB).
CDC plays a vital role in preventing and controlling epidemics in the United
States and across the globe. In 2003, when the President's Emergency Plan for
AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) was announced, CDC GAP joined the unified US Government
response to global HIV/AIDS. Because of its presence on the ground, CDC GAP also
is uniquely positioned to coordinate with and draw upon the strengths of CDC's
other global health programs, such as global disease detection, public health
training, and prevention and control of other infectious diseases such as
malaria and tuberculosis (TB).
Today, CDC GAP has more than 100 staff based in its Atlanta headquarters, has
assigned more than 100 CDC staff to the field, and has employed more than 1,000
local staff to implement country programs. CDC GAP field offices support
HIV/AIDS prevention, care, treatment, and capacity building efforts as a member
of the interagency team implementing the PEPFAR.
Prevention
- Preventing Medical HIV Transmission: Through PEPFAR, CDC GAP supports national programs to improve the quality and sustainability of blood supplies and reduce the incidence of unsafe injections.
- HIV Counseling and Testing: CDC GAP assists countries to strengthen their HIV counseling and testing efforts by providing training for HIV counseling and testing; program planning and implementation; quality assurance and program management; and monitoring and evaluation.
- Promoting Safe Behaviors: CDC GAP supports a variety of prevention interventions for HIV-infected individuals and their families, youth and their parents, the broader community, and populations at risk to understand how to reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
Care and Treatment
- Preventing Mother-to-child HIV Transmission: CDC GAP supports national scale-up of prevention of mother-to-child HIV transmission (PMTCT) programs by working with governments to develop and implement national PMTCT policies, programs, training curriculums, and testing and counseling manuals, and to monitor and evaluate PMTCT programs.
- Providing Antiretroviral Treatment (ART) for Adults and Children: CDC GAP applies its scientific expertise and support to promote quality care and treatment of HIV-infected individuals in PEPFAR-supported countries by influencing public policy, health care practice, community services, and individual behaviors.
- Supporting Care for People Living with HIV and Those Co-Infected with TB and HIV: CDC GAP's care and treatment priorities include interventions to improve the quality of life for people living with HIV and AIDS and their families. Complementary to ART, care begins with the diagnosis of HIV infection and continues throughout the course of the disease. CDC GAP care efforts include community mobilization; leadership development of people living with HIV/AIDS; and legal services, linkages to food support, and income-generating programs.
Laboratory Capacity and Strategic Information
- Supporting Surveillance Efforts: CDC GAP supports countries' surveillance efforts so they can assess the extent, trends, and impact of their HIV epidemics and also the success of their HIV prevention, treatment, and care efforts.
- Monitoring and Evaluation of Program Activity: CDC GAP helps to strengthen country monitoring systems that track program service delivery and supports evaluation studies.
- Statistics and Data Management: CDC GAP's helps countries to build effective and sustainable use of their health information management infrastructure.
- Building Laboratory Capacity: CDC GAP partners with Ministries of Health to strengthen the capacity of national laboratory systems to provide effective diagnosis, monitoring, and surveillance of HIV infection through support for supplies and equipment and the training of laboratory staff.
- Strengthening Human Capacity: CDC GAP works with Ministries of Health and international partners to develop high-quality standardized training curriculums and programs to build the cadre of local service providers required to successfully combat this disease. In addition, CDC GAP strengthens countries' capacities to plan, conduct, and evaluate their own training efforts.
Last modified:
October 28, 2008
Last reviewed:
October 28, 2008
Content Source:
Global AIDS Program (GAP)
National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention
