Energy and You
The benefits of clean energy include:
- Reduced emissions of air pollution and greenhouse gases
- Lower consumer energy bills
- Enhanced state and local economic development and job creation
- Improved reliability and security of our nation’s energy system
Today, more than ever, consumers have the ability and the interest to choose clean energy, including energy efficiency, renewable energy, and efficient combined heat and power. These options can help you stabilize or reduce your energy bills, which have been rising in many areas in recent years.
EPA’s Clean Energy Web site can help you understand what clean energy is, how energy use affects the environment, what your personal impact is, and how you can help mitigate that impact.
Just follow the links below to find out more!
- What is the impact of electricity generation on the environment?
- How clean is the electricity I use? (Power Profiler)
- How can I reduce my impact?
What Is the Impact of Electricity Generation on the Environment?
Of the total energy consumed in America, about 39% is used to generate electricity. Therefore, electricity consumption is an important portion of a consumer's environmental footprint.
All forms of electricity generation have some level of environmental impact. As the chart below shows, most of the electricity in the United States is generated from fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas and oil.
Fuel Mix for U.S. Electricity Generation
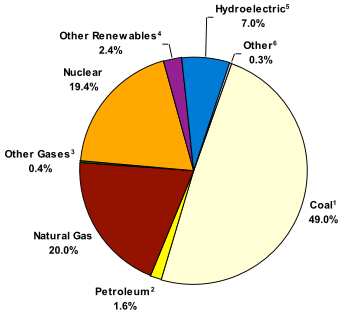
Source: Energy Information Administration. 2007. Electric Power Annual 2006. DOE/EIA-0348(2006). Washington, DC. Available at http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/electricity/epa/epa.pdf (95 pp., 2.6M, About PDF) and http://www.eia.doe.gov/cneaf/electricity/epa/figes1.html.
Using energy more efficiently through more efficient products, such as ENERGY STAR qualified appliances or light bulbs, or through more efficient generation, such as Combined Heat and Power, reduces the amount of fuel required to produce a unit of energy output and reduces the corresponding emissions of pollutants and greenhouse gases. Electricity from renewable resources such as solar, geothermal, and wind technologies generally does not contribute to climate change or local air pollution since no fuels are combusted in these processes.
To read more about the impacts of electricity use on the environment visit How does electricity use affect the environment?
There are also opportunities to reduce your environmental impact in the transportation sector, for more information visit www.epa.gov/otaq.
How Clean Is the Electricity I Use?
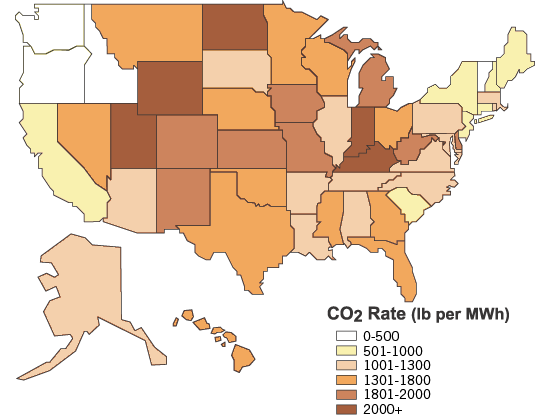
The emissions caused by power generation vary from state to state, depending on the electricity generation technologies used in the region. The map below shows state-specific emission rates for carbon dioxide, an important greenhouse gas associated with global climate change.
You can use the Power Profiler to generate a report about your own electricity use, like the one shown below. All you need is your zip code. The Power Profiler takes about five minutes to run. Enter the Power Profiler »
How Can I Reduce My Impact?
Reducing the environmental impacts of your energy use is easy and can be done by making good energy decisions.
- Quick steps to reduce energy use in your home and at the office
- Clean energy information for small business
- Anthracite, bituminous coal, subbituminous coal, lignite, waste coal, and synthetic coal.
- Distillate fuel oil (all diesel and No. 1, No. 2, and No. 4 fuel oils), residual fuel oil (No. 5 and No. 6 fuel 7% Hyoils and bunker C fuel oil), jet fuel, kerosene, petroleum coke (converted to liquid petroleum) and waste oil.
- Blast furnace gas, propane gas, and other manufactured and waste gases derived from fossil fuels.
- Wood, black liquor, other wood waste, biogenic municipal solid waste, landfill gas, sludge waste, agriculture byproducts, other biomass, geothermal, solar thermal, photovoltaic energy, and wind.
- Total of conventional hydroelectric power and hydroelectric power from pumped storage facilities.
- Non-biogenic municipal solid waste, batteries, chemicals, hydrogen, pitch, purchased steam, sulfur, tire-derived fuels and miscellaneous technologies.
![[logo] US EPA](https://webarchive.library.unt.edu/eot2008/20081108113326im_/http://www.epa.gov/epafiles/images/logo_epaseal.gif)