USAID Boosts Emergency Obstetric and Newborn Care in Nigeria
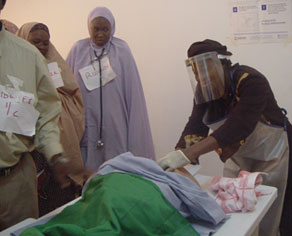 |
Health care providers practice providing emergency obstetric and newborn care (EmONC) during a three-week training in Gusau, Zamfara State of Nigeria.
Source: Gombe Ibrahim/JHPIEGO |
From March 11 to April 6, 2007 in Gusau, Zamfara State of Nigeria, USAID trained four doctors and seven health care providers (nurses and midwives) in emergency obstetric and newborn care (EmONC) services to strengthen the performance of health care providers in USAID-funded facilities there.
Maternal mortality remains a major health problem in Nigeria. Increasing the proportion of births attended by a qualified health worker, access to proper emergency obstetric care (EOC), and sponsorship of community-based maternal and newborn care interventions are keys to reducing maternal mortality. USAID supports obstetric care services that are acceptable to the community and which mothers-to-be utilize. The Agency is working with the Government of Nigeria and other donors in Nigeria to increase skilled attendance at birth, provide emergency obstetric care, use clean childbirth practices and essential newborn care (drying the baby, warmth, cleanliness and early exclusive breastfeeding) at home.
The first week of training was used for didactic sessions and clinical practice on a variety of anatomic models, while the remaining two weeks were spent in the King Fahd Hospital for hands-on practical sessions with clients.
USAID's neonatal health activities prioritize postpartum care in the home soon after birth to address the immediate needs of both mother and newborn. Appropriate behavior change communications programs address recognition of danger signs in the newborn and mothers and the importance of seeking care to prevent infant and maternal death, which are very common during a time of fragile status for both baby and mother. Other messages encourage good self care including hygiene, sanitation, nutrition, and bed net use in malaria areas.
|


