|

Press Release 07-143
Getting Light to Bend Backwards

Uniquely sandwiched materials coax light to defy nature and skirt the laws of refraction
October 16, 2007
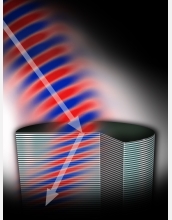
While developing new lenses for next-generation sensors, researchers have crafted a layered material that causes light to refract, or bend, in a manner nature never intended. Refraction always bends light one way, as one can see in the illusion of a "bent" drinking straw when observed through the side of a glass. A new metamaterial crafted from alternating layers of semiconductors (indium-gallium-arsenic and aluminum-indium-arsenic) acts as a single lens that refracts light in the opposite direction. Refraction is the reason that lenses have to be curved, a trait that limits image resolution. With the new metamaterial, flat lenses are possible, theoretically allowing microscopes to capture images of objects as small as a strand of DNA. The current metamaterial lens works with infrared light, but the researchers hope the technology will expand to other wavelengths in the future. Earlier efforts have crafted metamaterials that bend light in a similar way, but this is the first to do so using a 3-dimensional structure and a metamaterial comprised entirely of semiconductors. Those traits will prove critical for incorporating the technology into devices such as chemical threat sensors, communications equipment and medical diagnostics tools. The paper describing the technology appeared online Oct. 14, 2007, in Nature Materials. The research was developed primarily at NSF's Mid-Infrared Technologies for Health and the Environment Engineering Research Center and NSF's Princeton Center for Complex Materials Materials Research Science and Engineering Center. Additional information is available in the Princeton University press release at: http://www.princeton.edu/main/news/archive/S19/21/37O65/
-NSF-

Media Contacts
Joshua A. Chamot, NSF (703) 292-7730 jchamot@nsf.gov
Hilary Parker, Princeton University (609) 258-4597 haparker@princeton.edu
Program Contacts
Maija M. Kukla, NSF (703) 292-4940 mkukla@nsf.gov
Lynn Preston, NSF (703) 292-5358 lpreston@nsf.gov
Principal Investigators
Claire Gmachl, Princeton University (609) 258-3500 cgmachl@princeton.edu

The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that
supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and
engineering, with an annual budget of $6.06 billion. NSF funds reach all 50
states through grants to over 1,900 universities and institutions. Each year,
NSF receives about 45,000 competitive requests for funding, and makes over
11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards over $400 million in
professional and service contracts yearly.
 Get News Updates by Email Get News Updates by Email
Useful NSF Web Sites:
NSF Home Page: http://www.nsf.gov
NSF News: http://www.nsf.gov/news/
For the News Media: http://www.nsf.gov/news/newsroom.jsp
Science and Engineering Statistics: http://www.nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards Searches: http://www.nsf.gov/awardsearch/
|