DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE
The President’s 2009 Budget will:
-
Advance technological innovation
through the President’s American Competitiveness Initiative;
-
Open new markets for U.S. exporters, protect intellectual
property rights, obtain compliance with trade agreements, and enforce
unfair trade laws;
-
Support critical demographic and economic statistics,
including the 2010 Decennial Census;
-
Enhance understanding of the planet’s weather
and climate;
-
Improve stewardship of ocean and coastal resources
and wildlife; and
-
Restrain spending in lower-priority areas.
Advancing U.S. Competitiveness through Technological Innovation,
Free Trade, and Intellectual Property Protection
-
Supports the American Competitiveness
Initiative. Provides $634 million for investments in quantum
and neutron research, nanotechnology, and related scientific work
at the National Institute of Standards and Technology, a 20-percent
increase over the 2008 enacted level, excluding earmarks and unrequested
grants.
-
Facilitates the transition
to digital television broadcasts. Ensures a smooth transition
from analog to digital television broadcasts by February 18, 2009,
through information and assistance efforts, thereby clearing valuable
radio spectrum to enhance the capabilities of first responders and
bring greater choice to media and telecommunications consumers.
-
Advances free trade. Opens and expands new markets for U.S. goods and services, helps
develop and enforce free trade agreements with other nations, eliminates
barriers to sales of U.S. products, and improves the competitiveness of U.S. firms. Disseminates
advanced U.S. clean energy technologies throughout the Asia-Pacific
region by hosting trade missions and other outreach events.
-
Protects intellectual property
rights. Combats global piracy and counterfeiting, and
strengthens the United States Patent and Trademark Office to support
efforts to safeguard the value of intellectual property through more efficient and higher quality
patent and trademark examinations.
Improving Public and Private-Sector Decisions with Enhanced
Data
-
Prepares for the 2010 Decennial
Census. Opens field offices and finalizes systems for
the population count in spring
2010, which is called for in Article I of the Constitution.
-
Improves economic data. Promotes more accurate data on the contributions of the health care
sector and research and development to gross domestic product (GDP),
and also significantly improves measurement of the service sector.
Enhancing the Ability to Observe, Protect, and Manage the Earth’s
Resources
-
Improves weather forecasting
and global climate monitoring. Provides $981 million to
develop and acquire vital weather satellites and climate sensors (an
increase of $175 million over the 2008 request and $220 million over
the enacted level) and $31 million over the 2008 request in new initiatives
to improve forecasts of severe weather, fires, and droughts.
-
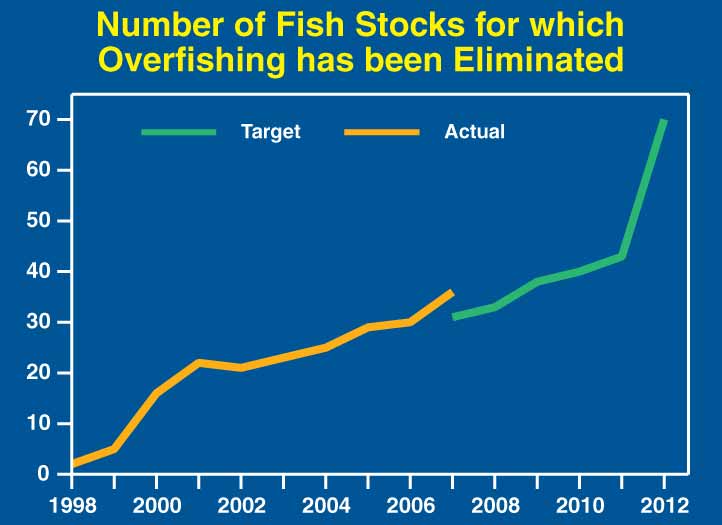
Protects oceans and manages
natural resources. Increases funding for last year’s
initiative supporting the Ocean Action Plan by $31 million over the
2008 request, to $154 million. These funds will enhance fisheries
management and support the Magnuson-Stevens Act requirement of eliminating
overfishing by 2011, as well as strengthen efforts to advance ocean
observing networks, study ocean acidification, reduce harmful marine
debris, support maritime commerce, and protect marine mammals.
Major Savings and Reforms
Since 2001, the Department of Commerce has:
-
Vigorously contributed to the Administration’s
free-trade agenda, leading to the signing or completion of free trade
agreements with 17 countries that feature increased intellectual property
protections and expanded access for U.S. products and services. From
2001 to 2006, annual U.S. exports increased by $440 billion (nearly
30 percent in constant dollars), which benefits businesses of all
sizes and American workers.
-
Enforced trade agreements by initiating 286 antidumping
or countervailing duty investigations and applied anti-subsidy countervailing
duty investigations on imports from emerging non-market economies
for the first time in 23 years.
-
Enhanced the quality and timeliness of key economic
data; for example, making GDP information on a State-by-State basis
available 12 months earlier.
-
Supported sound management of fisheries and related
ocean resources, including protecting over 7,000 species within the
world’s largest marine protected area—the Papahanaumokuakea
Marine National Monument in Hawaii.
-
Improved weather forecasting and climate science capabilities,
such as increasing the lead time for winter storm warnings from 9
hours in 2000 to 19 hours in 2007.
Department of Commerce
(Dollar amounts in millions)
| |
2007
Actual |
Estimate |
| 2008 |
2009 |
| Spending |
|
|
|
| Discretionary
Budget Authority: |
|
|
|
| Departmental Management: |
|
|
|
| Salaries and Expenses |
49 |
44 |
61 |
| Emergency Steel
Guaranteed Loan Program |
— |
— |
−49 |
| Headquarters Renovation |
— |
4 |
7 |
National Intellectual
Property Law Enforcement Coordination
Council |
— |
— |
1 |
| Office of the
Inspector General |
23 |
22 |
25 |
| Subtotal, Departmental
Management |
72 |
70 |
45 |
| Economic Development
Administration |
281 |
274 |
133 |
| Bureau of the
Census |
893 |
1,230 |
2,605 |
| Economics and
Statistics Administration |
80 |
80 |
91 |
| International
Trade Administration |
402 |
405 |
420 |
| Bureau of Industry
and Security |
75 |
73 |
84 |
| Minority Business
Development Agency |
30 |
29 |
29 |
| National Oceanic
and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): |
|
|
|
| Operations, Research,
and Facilities |
2,821 |
2,933 |
2,913 |
| Procurement, Acquisition
and Construction |
1,085 |
971 |
1,239 |
| Other accounts |
−11 |
68 |
−42 |
| Subtotal, NOAA |
4,065 |
3,972 |
4,110 |
| U.S. Patent and
Trademark Office (PTO): |
|
|
|
| Program level |
1,779 |
1,916 |
2,075 |
| Fees |
−1,791 |
−1,916 |
−2,075 |
| Subtotal, PTO |
−12 |
— |
— |
| Technology Administration |
2 |
— |
— |
|
|
|
|
|
| National Institute
of Standards and Technology (NIST): |
|
|
|
| Scientific and
Technical Research and Services |
439 |
446 |
539 |
| Industrial Technology
Services |
177 |
136 |
4 |
| Construction of
Research Facilities |
59 |
160 |
99 |
| Subtotal, NIST |
675 |
742 |
642 |
| National Telecommunications
and Information Administration |
40 |
36 |
19 |
| Discretionary
offsetting receipts |
−23 |
−4 |
−1 |
| Total, Discretionary
budget authority |
6,410 |
6,907 |
8,177 |
| |
|
|
|
| Memorandum: Budget authority from enacted supplementals |
170 |
— |
— |
| |
|
|
|
| Total, Discretionary
outlays |
6,418 |
7,145 |
8,072 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Mandatory Outlays: |
|
|
|
| Digital Television
Fund programs: |
|
|
|
| Public Safety
Interoperable Communications grants |
24 |
296 |
396 |
| Digital Television
Converter Box program |
36 |
404 |
534 |
| Other programs |
— |
152 |
102 |
| All other |
8 |
162 |
151 |
| Mandatory offsetting
receipts 1 |
— |
−852 |
−1,032 |
| Total, Mandatory
outlays |
68 |
162 |
151 |
| |
|
|
|
| Total, Outlays |
6,486 |
7,327 |
8,223 |
| |
|
|
|
| Credit activity |
|
|
|
| Direct Loan Disbursements: |
|
|
|
| Fisheries Finance
Direct Loan Financing account |
84 |
52 |
39 |
| |
|
|
|
| |
Number of Programs |
|
2009 Savings |
Major Savings, Discretionary |
|
|
|
| Terminations |
4 |
|
−200 |
| Reductions |
2 |
|
−175 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 Mandatory offsetting receipts include spectrum
auction receipts that fund mandatory programs in the National Telecommunications
and Information Administration created by the Deficit
Reduction Act of 2005.
|
 Skip Main Navigation
Skip Main Navigation