|
Following is the slide set of HIV Surveillance data among Men who have Sex with Men (MSM), through 2006. This slide set conveys important information on new and prevalent HIV and AIDS diagnoses among MSM in the United States. It does not include HIV incidence data, which is being compiled in a separate slide set. HIV incidence is the number of people who become newly infected with HIV in a given period of time while HIV diagnoses are the number of people with a new diagnosis of HIV infection regardless of when they were infected. Information on both diagnoses and incidence can be used together to help guide program planning and evaluate existing programs.
Instructions for downloading and using
HIV/AIDS surveillance slides.
Download the
complete slide set:
While the content is in the public domain and
no copyright restriction applies,
we do ask that users preserve the slides in
their current format and cite CDC as the
source.
|
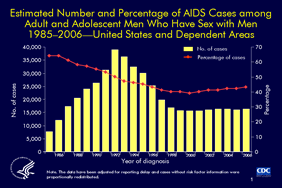
Slide 1
Estimated Number and Percentage of AIDS Cases among Adult and Adolescent Men Who Have Sex with Men
1985–2006—United States and Dependent Areas
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|

Slide 2
Estimated AIDS Cases in Males,
Cumulative through 2006—50 States and DC
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File
or
PPT
File |
|
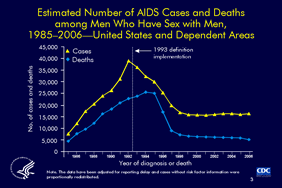
Slide 3
Estimated Number of AIDS Cases and Deaths
among Men Who Have Sex with Men,
1985–2006—United States and Dependent Areas
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|
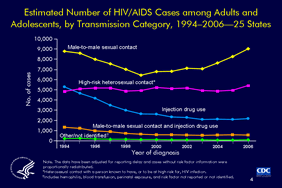
Slide 4
Estimated Number of HIV/AIDS Cases among Adults and Adolescents, by Transmission Category, 1994–2006—25 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|

Slide 5
Estimated Number and Proportion of HIV/AIDS Cases
among Adults and Adolescents
by Transmission Category, 2006—33 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|
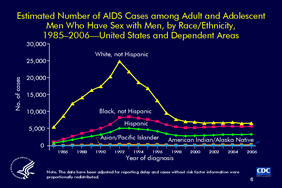
Slide 6
Estimated Number of AIDS Cases among Adult and Adolescent Men Who Have Sex with Men, by Race/Ethnicity,
1985–2006—United States and Dependent Areas
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|
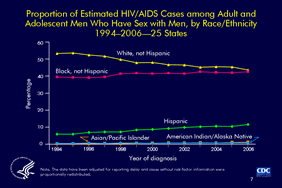
Slide 7
Proportion of Estimated HIV/AIDS Cases among Adult and
Adolescent Men Who Have Sex with Men, by Race/Ethnicity
1994–2006—25 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|

Slide 8
Estimated Number of Adult and Adolescent Men
Who Have Sex with Men Living with HIV/AIDS
by Race/Ethnicity, 2001–2006—33 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File
or
PPT
File |
|
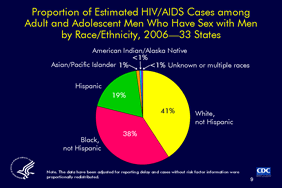
Slide 9
Proportion of Estimated HIV/AIDS Cases among
Adult and Adolescent Men Who Have Sex with Men
by Race/Ethnicity, 2006—33 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|
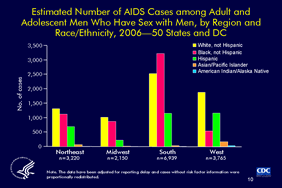
Slide 10
Estimated Number of AIDS Cases among Adult and
Adolescent Men Who Have Sex with Men, by Region and
Race/Ethnicity, 2006—50 States and DC
PDF File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|
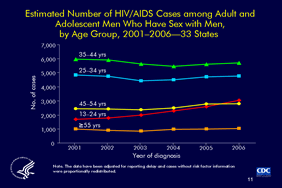
Slide 11
Estimated Number of HIV/AIDS Cases among Adult and
Adolescent Men Who Have Sex with Men,
by Age Group, 2001–2006—33 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|
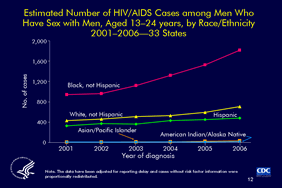
Slide 12
Estimated Number of HIV/AIDS Cases among Men Who
Have Sex with Men, Aged 13–24 years, by Race/Ethnicity
2001–2006—33 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|
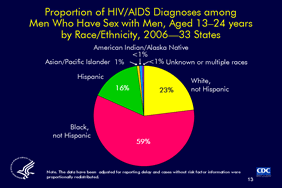
Slide 13
Proportion of HIV/AIDS Diagnoses among
Men Who Have Sex with Men, Aged 13–24 years
by Race/Ethnicity, 2006—33 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|

Slide 14
Estimated Number of HIV/AIDS Cases among Adult and Adolescent Men Who Have Sex with Men
by Race/Ethnicity and Population of Area of Residence, 2006—33 States
PDF
File
 or
PPT
File or
PPT
File |
|