Electrical Burns
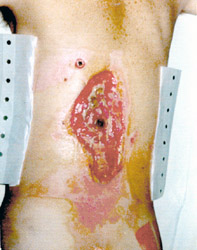
- Entrance Wound: High resistance of skin transforms electrical energy into heat, which produces burns around
the entrance point (dark spot in center of wound). This man was lucky, the current narrowly missed his spinal cord.
|
 |
- Exit Wound: Current flows through the body from the entrance point, until finally exiting where the body is
closest to the ground. This foot suffered massive internal injuries, which weren't readily visible, and had to be
amputated a few days later.
|

|
Arc or Flash Burns
- This man was near a power box when an electrical explosion occurred. Though he did not touch the box, electricity arced
through the air and entered his body. The current was drawn to his armpits because perspiration is very conductive.
|
 |
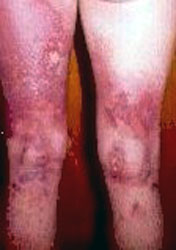
Thermal Contact Burns
- Current exited this man at his knees, catching his clothing on fire and burning his upper leg.
|
 |
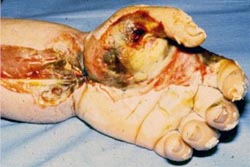
Internal Injuries
- This worker was shocked by a tool he was holding. The entrance wound and thermal burns from the overheated tool are
apparent
|
 |
- Same hand a few days later, when massive subcutaneous tissue damage had caused severe swelling (swelling usually
peaks 24-72 hours after electrical shock). To relieve pressure which would have damaged nerves and blood vessels, the
skin on the arm was cut open.
|
 |
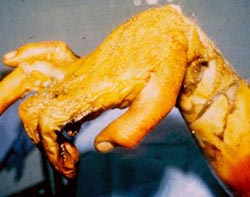
Involuntary Muscle Contraction
- This worker fell and grabbed a powerline to catch himself. The resulting electric shock mummified his first two
fingers, which had to be removed. The acute angle of the wrist was caused by burning of the tendons, which contracted,
drawing the hand with them.
|
 |

