1926 Subpart K
Overview
OCCUPATIONAL
SAFETY AND HEALTH 1926
Subpart K
Overview for Subpart K
Electrical
K-1 What are the most frequently cited
serious violations?
- §1926.403(a)-Electric equipment must be approved by an OSHA accepted
laboratory or agency.
- §1926.403(b)-Electric equipment must be free from recognized hazards
and used in accordance with manufacturers and approval agency instructions.
- §1926.403(I)(2) & (j)-Live parts of electric equipment operating
at more than 50 volts must be guarded from contact by an approved enclosure
or by other approved means. (See §1926.405(a)(2)(ii)(E), (a)(2)(iii),
and (b) for specific guarding requirements for lamps on temporary wiring,
for temporary wiring over 600 volts, and for electrical boxes, respectively.)
- §1926.404(b)(1)-Employers must provide either ground-fault circuit
interrupters or an assured equipment grounding conductor program.
- §1926.404(f)-Electric equipment must be grounded under the conditions
and in the manner given in Subpart K.
- §1926.405(a)(2)(ii)(J)-Extension cord sets used with portable tools
and appliances must be of the three-wire, grounding type; and flexible
cords must be designed for hard or extra-hard usage.
- §1926.405(g)(2)(iv)-Flexible cords must be provided with strain relief.
- §1926.416(a)-The employer must determine the location of electric
circuits that might be contacted during the course of work and must
implement measures to protect employees from accidental contact.
- §1926.416(e)(1)-Worn or frayed electric cords and cables may not be
used.
K-2 What are effective control measures that can be used to control
the hazard listed in K-1?
- Make sure that electric equipment is listed or labeled by an Agency
or testing laboratory acceptable to OSHA.
- Use electric equipment in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Install electric equipment with exposed live parts inside approved enclosures,
or install exposed live parts in such a manner that unqualified employees
cannot readily gain access to them (for example, by installation at
a height of 8 feet or more above the floor).
- Make sure that all non-double-insulated electric equipment is equipped
with a grounding conductor. Maintain the equipment grounding conductor
in good, operable condition.
- Provide either ground-fault circuit interrupters (see illustration
K) or an assured equipment grounding conductor program (which includes
the regular testing of all equipment grounding conductors) to protect
employees from ground faults.
- Use only three-wire extension cords sets, which provide an equipment
grounding conductor. (This applies regardless of whether they are used
"only" with double-insulated tools and equipment.) Use flexible cords
and cables that are marked with one of the following types: S, SC, SCE,
SCT, SE, SEO, SEOO, SJ, SJE, SJEO, SJEOO, SJO, SJT, SJTO, SJTOO, SO,
SOO, ST, STO, STOO, G, PPE, or W.
- Provide strain relief where flexible cords are connected to devices
and fittings to prevent pull from being applied directly to joints or
terminal screws.
- Determine, by direct observation, by inquiry, or by the use of instruments,
whether energized electric circuits are present in a work area where
they might be contacted by employees. Deenergize and ground the circuits
or guard them, or use insulation to protect employees. Inform employees
of the presence and location of these circuits.
- Inspect flexible cords for damage, and discard or repair any that
are worn or frayed or that have damaged insulation.
K-3 What work practices are needed for protection against electrical
hazards?
- Maintain a 10-foot-minimum clearance from overhead power lines (§§1926.416,
1926.550(a)(15), and 1926.600(a)(6)).
- Use barriers or other forms of guarding when live parts of electric
equipment and circuits are exposed (§1926.416(b)(1)).
- Maintain electric equipment in good condition (§§1926.416(e)(1) and
1926.431).
- Lockout and tag electric circuits that are to be deenergized (§1926.417).
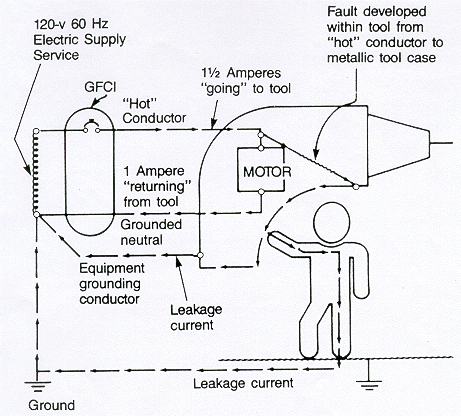
Illustration K
Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter
GFCI monitors the difference in current
flowing into the "hot" conductor and out to the grounded neutral conductor.
The difference (1/2 ampere in this case) will flow back through any available
path, such as the equipment grounding conductor, and through a person
holding the tool, if the person is in contact with a grounded object.
|