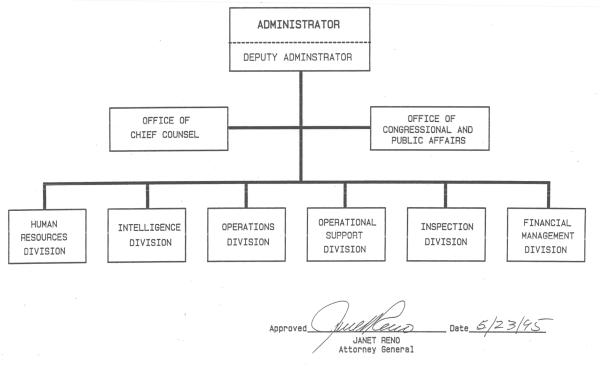
DRUG ENFORCEMENT ADMINISTRATION
 d
d
In 1968 the Justice Department’s Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs was formed. The organization then was composed of personnel from the Federal Bureau of Narcotics (Treasury Department) and the Bureau of Drug Abuse Control (Food and Drug Administration) of the Department of Health, Education and Welfare. In 1973 the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) was created by merging the Bureau of Narcotics and Dangerous Drugs, the Office for Drug Abuse Law Enforcement, the Office of National Narcotics Intelligence, elements of the U.S. Customs Service that worked in drug trafficking intelligence and investigations, and the Narcotics Advance Research Management Team.
The mission of the DEA is to enforce the controlled substances laws and regulations of the United States and to bring to the criminal and civil justice systems of the United States, or any other competent jurisdiction, those organizations, and principal members of organizations, involved in the growing, manufacture, or distribution of controlled substances appearing in or destined for illicit traffic in the United States; and to recommend and support non-enforcement programs aimed at reducing the availability of and demand for illicit controlled substances on the domestic and international markets.
In carrying out its mission as the agency responsible for enforcing the controlled substance laws and regulations of the United States, DEA’s primary responsibilities include:
- Investigation and preparation for the prosecution of major violators of controlled substances laws operating at interstate and international levels.
- Management of a national drug intelligence network in cooperation with federal, state, local, and foreign officials to collect, analyze, and disseminate strategic, investigative, and tactical intelligence information to U.S. law enforcement and intelligence agencies, and, when appropriate, to foreign counterparts.
- Seizure and forfeiture of assets derived from, traceable to, or intended to be used for illicit drug trafficking.
- Enforcement of the provisions of the Controlled Substances Act as they pertain to the manufacture, distribution, and dispensing of legally produced controlled substances.
- Coordination and cooperation with federal, state, local, and foreign law enforcement officials on mutual drug enforcement efforts.
- Coordination and cooperation with other federal, state, and local agencies and with foreign governments in programs designed to reduce the availability of drugs on the U.S. market through development of drug enforcement institutions and enhancement of drug enforcement agencies’ capabilities as well as through the development and promotion of non-enforcement methods such as crop eradication and demand reduction.
- Responsibility, under the policy guidance of the Secretary of State and U.S. Ambassadors, as the single point of contact for the coordination of all programs associated with drug law enforcement counterparts in foreign countries.
- Liaison with the United Nations, INTERPOL, and other organizations on matters relating to international drug control programs.
Drug Enforcement Administration Field Divisions
 d
d
Click on map for larger version
Return to the table of contents
 d
d