|
Electricity Generation
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Last Updated: September 2008 Next Update: December 2008 |
|||||||||||||
|
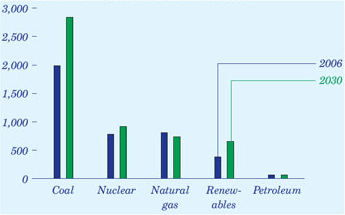
Consumers expect electricity on demand. We plug in an appliance or turn on a switch without giving it a second thought. To ensure that continuous flow of electricity is there to meet our needs, electric power producers operate several types of large generators. (For more on the amount of generators needed, see discussion on Electricity Capacity.) Mild temperatures in 2006 dampened the demand for electricity. Less need for heating and air conditioning kept electricity generation virtually the same as in 2005. Most electricity in the United States is generated with steam turbines. Fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and petroleum (oil) are burned in large furnaces, heating water, to make steam. Steam turns blades of a turbine to generate electricity. Gas turbines, fueled by petroleum or natural gas, use hot gases produced from combustion to rotate turbines. Internal-combustion engines, fueled by diesel oil, are also used to spin generators to produce electricity. In 2006, coal generated the largest share of electricity - 49%. At 1,991 billion kilowatthours(kWh) of generation, this is nearly one and a half times the annual electricity consumption of all U.S. households (1,354 billion kWh). Natural gas generated the second largest share dropping nearly 50% from 2005. For historical trends, see generation table for 1949-2006. Nuclear-powered generation accounts for 19% share, nudged into third place in 2006 by natural gas. Similar to fossil-fueled steam turbines, heat from the fission of uranium in a reactor is used to make steam to drive the turbine. Hydroelectric generation uses flowing water to spin the turbine. In a falling water system, water is accumulated in reservoirs created by dams, then released. Run-of-the-river systems use the force of the river current. In 2006, hydroelectric generation had the fourth largest share (7%) of electricity production. All other renewables account for only 3% of electricity generation in 2006.
Coal-fired power plants continue to be the dominant source of electricity generation through 2030. The natural gas share of generation falls from 20 percent in 2006 to 14 percent in 2030, while the coal share increases from 49 percent to 54 percent. The generation share from renewable capacity increases by 32 percent from 2006 to 2030 and represents 13 percent of total electricity supply in 2030. With capacity additions and improvements in performance at existing nuclear facilities, nuclear generation also increases; however, the nuclear share of total generation falls slightly, from 19 percent in 2006 to 18 percent in 2030.
More information on this subject can be found in the following EIA publications:
|
|
||||||||||||