All Images


Press Release 07-134
Scientists to Sick Plants: Take Two Doses of an Aspirin-Like Hormone and Call Me in the Morning

Discovery could lead to development of crops with enhanced yield, heightened immunity and reduced need for pesticides
Back to article | Note about images
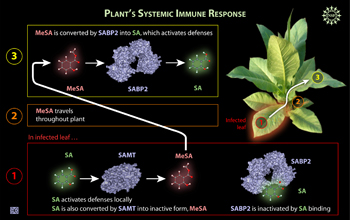 |
When a plant is infected by a pathogen, a plant hormone called salicylic acid (SA) activates defenses locally. Some of this SA is converted by an enzyme known as SAMT into an aspirin-like compound called methyl salicylate (MeSA) that travels to uninfected parts of the plant and thereby activates a plant-wide immune response. But some SA at the infection site binds to an enzyme called salicylic acid binding protein 2 (SABP2). This binding prevents the enzyme from converting SA at the infection site into biologically inactive MeSA.
Credit: Zina Deretsky, National Science Foundation |
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (840 KB)
|
Use your mouse to right-click (or Ctrl-click on a Mac) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
|
 |
Dan Klessig, Sang-Wook Park and Evans Kaimoyo examine a tobacco plant that was infected with tobacco mosiac virus during their study; their study lead to identification of an elusive signal for triggering plant-wide immunity. The signal is methyl salicylate, an aspirin-like compound.
Credit: Dan Klessig, Boyce Thompson Institute for Plant Research |
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (1 MB)
|
Use your mouse to right-click (or Ctrl-click on a Mac) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
|
|



