- NASA Home
- | Missions
- | Spitzer
- | Multimedia
Multimedia Features
Dance of the Light Echoes
05.29.08
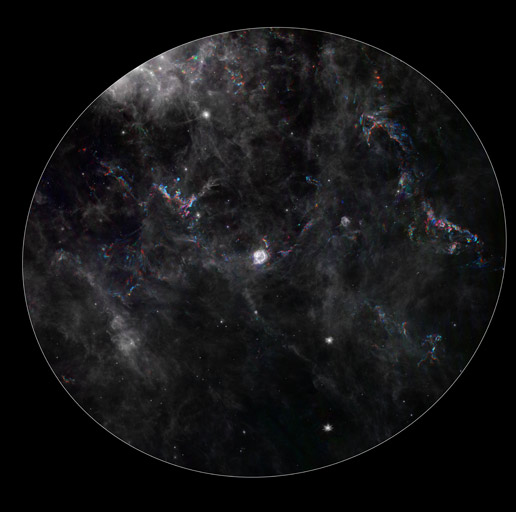
This composite image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the remnant of a star that exploded, called Cassiopeia A (center) and its surrounding "light echoes" -- dances of light through dusty clouds, created when stars blast apart. The light echoes are colored and the surrounding clouds of dust are gray.
A light echo occurs when a star explodes, acting like a cosmic flashbulb. The light from this explosion zips through nearby dust clumps, illuminating and heating them up slightly. This brief period of warming causes them to glow in infrared, like a chain of Christmas bulbs lighting up one by one. The result is an optical illusion, in which the dust appears to be flying outward at the speed of light.
Cassiopeia A is the remnant of a once massive star that died in a violent supernova explosion. It consists of a dead star, called a neutron star, and a surrounding shell of material that was blasted off as the star died. This remnant is located 11,000 light-years away in the northern constellation Cassiopeia.
This composite consists of six processed images taken over a time span of three years. Dust features that have not changed over time appear gray, while those that have changed are colored blue or orange. Bluer colors represent an earlier time and redder ones, a later time. The progression of the light echo through the dust can be seen here by the shift in colored dust clumps.
This light echo is the largest ever seen, stretching more than 300 light-years away from Cassiopeia A. If viewed from Earth, the entire frame would take up the same amount of space as seven full moons.
The earliest Spitzer image shown here was taken in February 2005, and the latest one in January 2008. The image was processed to emphasize the light echo by enhancing the areas that change, which appear in color, and dimming regions that remain constant, seen in grayscale. Spurious color artifacts such as diffraction spikes around stars were removed by hand.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
› High-resolution JPEG (4.5Mb)