| A Sensitive Zonagenetic Assay for Rapid in Vitro Assessment of Estrogenic Potency of Xenobiotics and Mycotoxins Trine Celius,1 Trine B. Haugen,2 Tom Grotmol,3 and Bernt T. Walther1 1Department of Molecular Biology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway
2Andrology Laboratory, Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, National Hospital, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway
3Institute for Epidemiological Cancer Research, Oslo, Norway Abstract
Mounting evidence confirms that hepatic biosynthetic processes are essential for female sexual maturation in fish, which is directly controlled by estrogens. These oogenetic events (zonagenesis and vitellogenesis) are induced in both sexes by estrogens. In this paper, we report the induction of zona radiata (zr) proteins and vitellogenin in primary hepatocytes from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) exposed to xenoestrogens and mycotoxins. Cells were treated with doses of 1, 5, and 10 µM 4-nonylphenol (4-NP) , o,p´-DDT, lindane (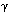 -HCH) , and bisphenol A (BPA) , which all induced zr proteins and vitellogenin in an approximate dose-dependent manner. Hepatocytes were also treated with combinations of xenoestrogens at 1 or 2 µM, resulting in elevated levels of both zr proteins and vitellogenin, compared to single treatment. The estrogenic activity of the mycotoxin zearalenone (ZEA) and its metabolites [ -HCH) , and bisphenol A (BPA) , which all induced zr proteins and vitellogenin in an approximate dose-dependent manner. Hepatocytes were also treated with combinations of xenoestrogens at 1 or 2 µM, resulting in elevated levels of both zr proteins and vitellogenin, compared to single treatment. The estrogenic activity of the mycotoxin zearalenone (ZEA) and its metabolites [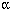 -zearalenol ( -zearalenol (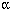 -ZEA) and ß-zearalenol (ß-ZEA) ], with regard to zonagenesis and vitellogenesis, was assessed in this assay system. Mycotoxins were used at concentrations of 10, 100, or 1,000 nM. All induced zr proteins and vitellogenin, with -ZEA) and ß-zearalenol (ß-ZEA) ], with regard to zonagenesis and vitellogenesis, was assessed in this assay system. Mycotoxins were used at concentrations of 10, 100, or 1,000 nM. All induced zr proteins and vitellogenin, with 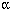 -ZEA being the strongest inducer. When cells were treated with xenoestrogens or mycotoxins in combination with an estrogen receptor inhibitor (ICI 182,780) , the induction of both zr proteins and vitellogenin was inhibited in all cases. Thus, the reported estrogen effects are bonafide estrogen responses. Zona radiata proteins were more responsive than vitellogenin to both xenoestrogens and mycotoxins. The versatility and sensitivity of the hepatocyte assay demonstrates that biosynthesis of zr proteins provides a new supplementary method for estimating xenoestrogenicity and mycotoxin action. Key words: eggshell, environmental chemicals, hepatocytes, mycotoxin, zearalenone, zonagenesis, zona radiata proteins. Environ Health Perspect 107:63-68 (1999) . [Online 10 December 1998] -ZEA being the strongest inducer. When cells were treated with xenoestrogens or mycotoxins in combination with an estrogen receptor inhibitor (ICI 182,780) , the induction of both zr proteins and vitellogenin was inhibited in all cases. Thus, the reported estrogen effects are bonafide estrogen responses. Zona radiata proteins were more responsive than vitellogenin to both xenoestrogens and mycotoxins. The versatility and sensitivity of the hepatocyte assay demonstrates that biosynthesis of zr proteins provides a new supplementary method for estimating xenoestrogenicity and mycotoxin action. Key words: eggshell, environmental chemicals, hepatocytes, mycotoxin, zearalenone, zonagenesis, zona radiata proteins. Environ Health Perspect 107:63-68 (1999) . [Online 10 December 1998] http://ehpnet1.niehs.nih.gov/docs/1999/107p63-68celius/ abstract.html Address correspondence to B. Walther, Department of Molecular Biology, University of Bergen, HIB, N-5920 Bergen, Norway. We thank B. Vose at ZENECA Pharmaceuticals for the support of ICI 182,780. We thank A. Goksøyr and A. Arukwe for help and comments. This study was supported by the Norwegian Research Council, Programme for Ecotoxicology. Received 20 May 1998 ; accepted 18 August 1998.
The full version of this article is available for free in HTML format. |

